On your logical standby database, you specified these rules:

After completion of the weekend batch cycle you attempt to delete the SQL Apply filters:
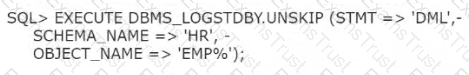
Which is TRUE regarding the execution of the UNSKIP procedure?
Which two are prerequisites for configuring Transaction Guard in a Data Guard environment?
Which two statements are true regarding asynchronous redo transport in a Data Guard
In Oracle Database 19c, you can set the value of database initialization parameters in a database using
the EDIT DATABASE... SET PARAMETER Command:
DGMGRL> EDIT DATABASE 'boston' SET PARAMETER log_archive_trace - 1;
Which THREE statements are TRUE about the command?
A customer asks for your recommendation regarding this requirement:
1. We plan to have a Data Guard Configuration with one primary database and one physical standby database.
2. We want zero data loss in case of a disaster involving the loss of one component.
3. We want to do Real Application Testing occasionally on the Standby Database.
Which solution, if any, satisfies these requirements?
Which three are true about using Flashback database through role transitions in a Data Guard environment?
Your expertise is requested for these customer requirements:
The Data Guard environment must be in maximum protection mode.
Reports must be offloaded to a physical standby database.
There must be no lag between the primary and standby databases that affect the reports produced.
The primary database must be resilient in case of a single network failure.
Which solution is correct for these requirements?
Which TWO observations are true about the Far Sync instance?
Examine the Data Guard configuration:

What happens if you issue "switchover to sheep;" at the DGMGRL prompt?
Which THREE statements are true about Far Sync instances?
Which three are true concerning database states after a successful switchover?
You must design an Oracle Data Guard configuration for a DSS database that meets these permanent
requirements:
1. Creating and maintaining bitmap indexes should not impact the performance of the primary database.
2. Creating and maintaining materialized views should not impact the performance of the primary database.
Additionally, there are these requirements, only one of which is ever done at any one time:
1. It should be possible to apply designated patches with a minimum amount of downtime.
2. Upgrading to a new database release should be performed with the least possible amount of downtime.
3. New application software releases should be tested against an exact and up-to-date replica of the primary database.
Which configuration meets these requirements with the fewest of databases?
You must configure on Oracle Data .......
1. A primary database
2. Three Physical Standby Databases
Examine these requirements:
A designated physical standby database should become the primary database automatically whenever the primary database fails.
2. The chosen protection mode should provide the highest level of protection possible without violating the other requirement.
Which redo transport mode and protection mode would you configure to meet these requirements?
You created a physical standby database prodsbyi from the primary database prod using SQL and RMAN. Which THREE are prerequisites for creating a Data Guard Broker configuration to manage these databases?
Which two factors can cause an increase in redo transport lag?
Your current Data Guard environment consists of:
A primary database containing no abstract data types used for user tables.
Two separate remote physical standby databases used for reporting.
Examine these requirements for adding a new standby database to this Data Guard environment:
The new standby database must provide a disaster recovery solution.
There must be minimal additional performance overheads on the primary database.
The new standby database may require additional indexes and materialized views not present in the primary.
New tables or schemas may be required in the standby database that are not present in the primary.
What would you recommend to fulfill these requirements?
Which feature is available when monitoring a Data Guard configuration using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, but is not available using DGMGRL or by using SQL?
Your Data Guard environment has two remote physical standby databases.
Client applications use the local naming method to connect to the primary database instance.
You want applications to automatically connect to the new primary database instance in case of a switchover or a failover.
Which set of actions will fulfill this requirement?
Which three statements are true……. With no Oracle Streams or Goldengate configured?
Which three statements are true about snapshot standby databases?
Which two are true concerning the configuring of Flashback database in a Data Guard environment?
Your Data Guard environment contains a primary database and three standby databases with these attributes:
1. prod : Primary database
2. prod_prq : Physical standby database with real-time query enabled used by reporting applications
3. prod_lsby: Logical standby database used by DSS
4. PROD_SSBY: Snapshot standby database used for Real Application Testing
Which TWO can be used to prevent clients from connecting to the wrong database instance?
Examine the Data Guard configuration:
DGMGRL> show configuration;
Configuration - Animals
Protection Mode: MaxAvailability
Databases:
dogs - Primary database
cats - Snapshot standby database
sheep - Snapshot standby database
Fast-Start Failover: DISABLED
Configuration Status:
ORA-01034: ORACLE not available
ORA-16625: cannot reach database "dogs"
DGM-17017: unable to determine configuration status
ou wish to perform a failover to sheep. Which command, or sequence of commands, should you issue to the broker before executing failover to sheep; using the broker?
The Oracle database 19c Observer is currently running on host1 and you wish to have it running on host2.
Examine this list of possible steps:
1) Stop the observer on host1
2) Disable Fast-Start Failover
3) Update the broker configuration with the new observer hostname
4) Enable Fast-Start Failover
5) Start the Observer on host2
Which contains the minimum required steps to move the observer to host2?
Which THREE statements are TRUE about Global Sequences when connected to a physical standby database with Real-Time Query enabled?
A Data Guard environment has this configuration and these attributes:
The primary database prima is in the local region.
A physical standby database physt1 is in the local region.
A physical standby database physt2 is in a remote region.
The primary ships redo to physt1.
physt1 ships redo to physt2.
physt1 and physt2 have Real-Time Query enabled.
A sequence has been created with this SQL statement in the primary database:
CREATE SEQUENCE a NOCACHE SESSION;
Which TWO statements are TRUE?
Which three statements are true about redo transport?
Which THREE statements are TRUE about the supported workload in Active Data Guard standby databases?
Attempting to start the observer raises an error:
DGMGRL> start observer;
DGM-16954: Unable to open and lock the Observer configuration file
Failed.
Identify two possible ways to start the observer successfully.
Which THREE are among the various tasks performed by the Data Guard Monitor (DMON) process?
You have a Data Guard Broker configuration called 'Somewhere' as shown:
DGMGRL> SHOW CONFIGURATION;
Configuration - Somewhere
Protection Mode: MaxPerformance
Databases:
Nearby - Primary database
FS - Far Sync
Farout - Physical standby database
Fast-Start Failover: DISABLED
Configuration Status:
SUCCESS
You then run this command:
DGMGRL> SHOW DATABASE 'Nearby' 'InconsistentProperties';
Which two are true about the output of this DGMGRL command?
You must propose an Oracle Data Guard configuration for a database supporting an OLTP workload that meets these permanent requirements:
Data loss is not permitted.
Read-only applications should not connect to the primary database instance.
Additionally, there are these requirements, only one of which is ever done at any one time:
It should be possible to apply and test designated patches with a minimum amount of downtime.
Upgrading to a new database release should be performed with the least possible amount of downtime.
New application software releases should be tested against an exact up-to-date replica of the production database.
You propose a primary database with one physical standby database configured in Maximum Protection mode.
Which requirements do you meet?