Patient safety is enhanced when alarms:
Fetal respiratory acidosis is most likely to present with which of the following fetal heart rate decelerations?
This fetal heart rate tracing is from a woman in the second stage of labor. This tracing is best interpreted as:
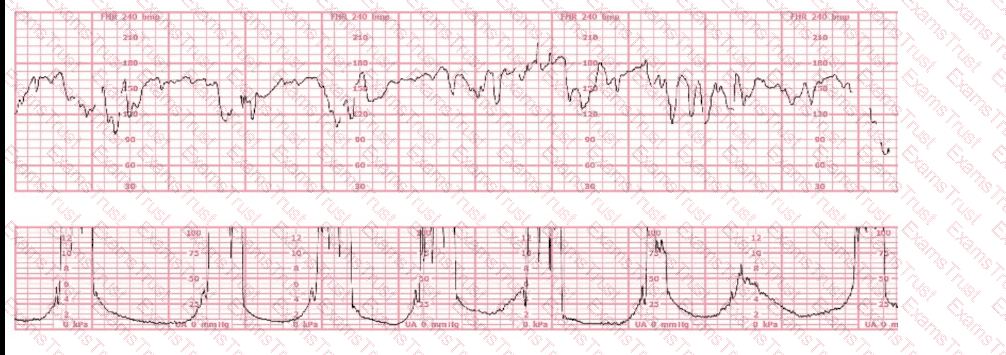
A woman (G1P0) arrives in triage with a pain score of 4/10 at 39-weeks gestation. The fetal heart rate tracing shown is obtained. The best intervention is to:
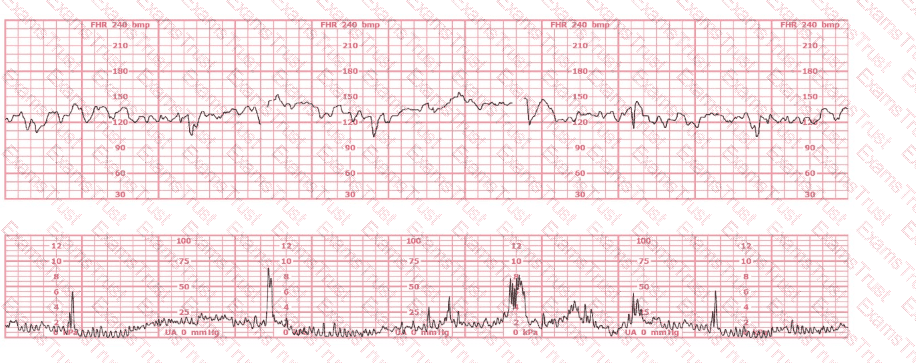
A patient presents at 38-weeks gestation with complaints of decreased fetal movement and ruptured membranes. The fetal heart rate is not able to be determined with an external ultrasound monitor. A spiral electrode is placed, and the tracing shows a rate of 90 bpm. What is the next most appropriate action?
(Full question)
This tracing would be categorized as a
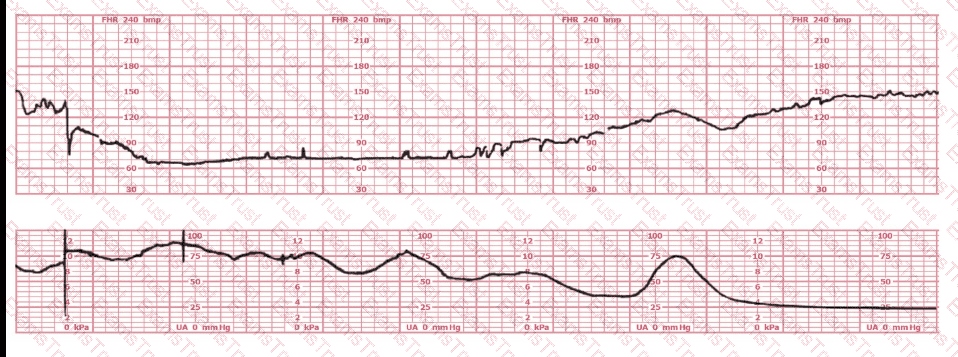
A fetal heart rate tracing is abnormal. A change in maternal position and oxygen administration do not correct the pattern. Following birth, a fetal cord blood sample is taken:
pH = 7.25
PaCO₂ = 46 mm Hg
PaO₂ = 20 mm Hg
HCO₃ = 22 mEq/L
Base deficit = –4 mEq/L
These results are best interpreted as:
A woman at 36-weeks gestation comes in because of uterine contractions radiating to the back. She has no insurance. In accordance with the Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA), she is obligated to be:
Maternal fever can cause fetal tachycardia because the increased maternal temperature:
The tracing shown is a:
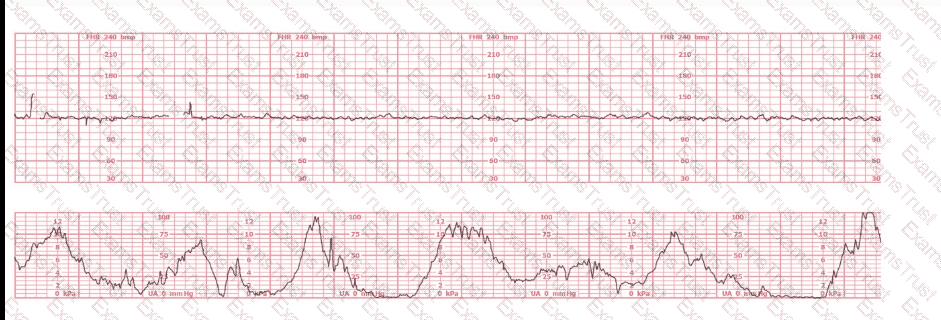
When evaluating a baseline fetal heart rate change, the fetal heart rate is assessed for a minimum of:
The decelerations seen in the fetal monitoring tracing shown are best described as:
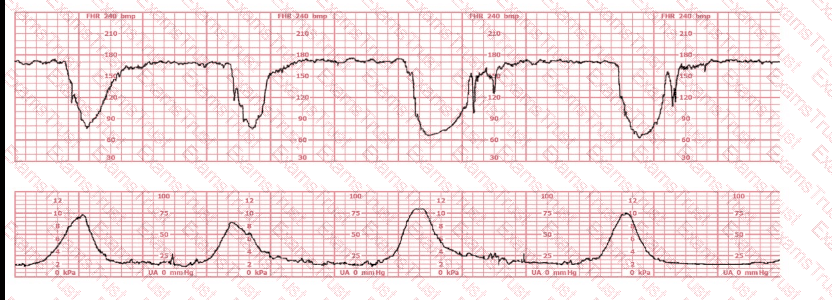
This tracing reflects
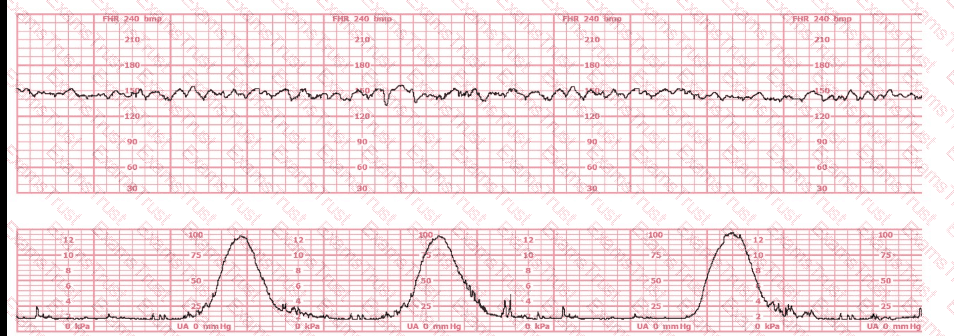
The fetal heart rate tracing shown represents
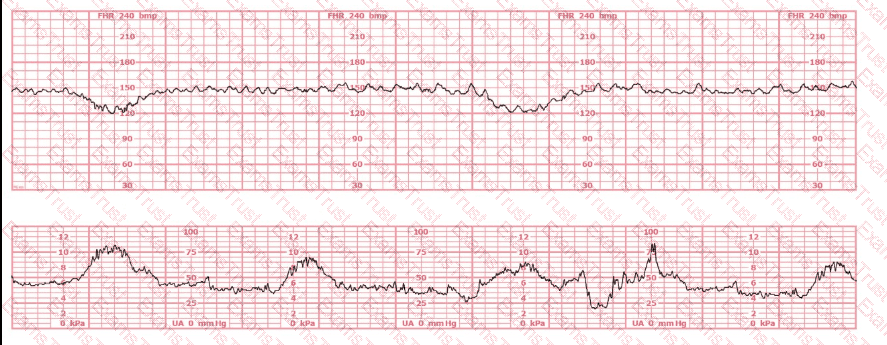
A 45-year-old woman at 36-weeks gestation presents for a nonstress test. Vital signs are:
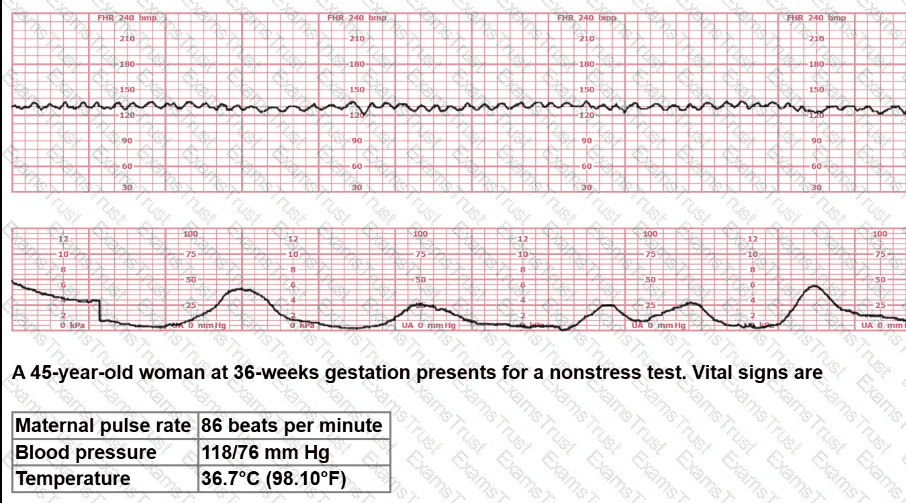
Maternal pulse rate: 86 beats per minute
Blood pressure: 118/76 mm Hg
Temperature: 36.7°C (98.1°F)
The next course of action would include:
Fetal supraventricular tachycardia will often appear on the monitor as
A woman has been 5 cm dilated for the past 3 hours. The tracing shown has developed over the last 30 minutes. The best initial course of action is to:
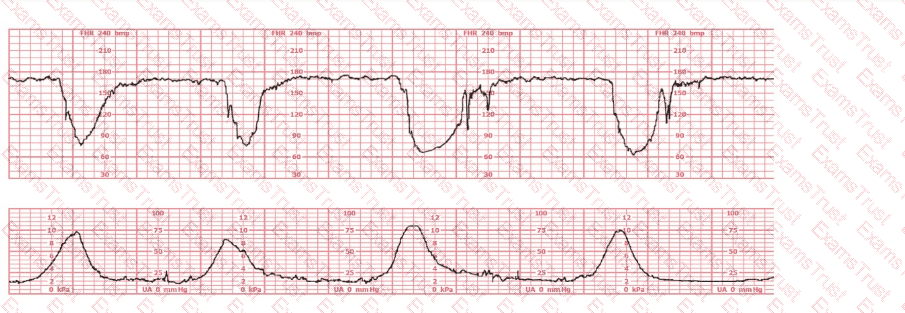
(Full question)
Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) is a useful intervention which can
This fetal heart rate tracing is of a woman in labor with dichorionic-diamniotic twins at 36-weeks gestation, 4 cm dilated. She is on oxygen via face mask. Based on the fetal heart rate tracing, what is the most appropriate action?
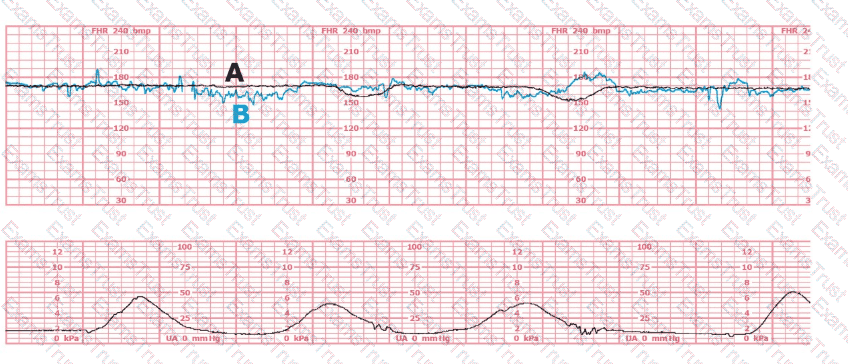
(Tracing A = black; Tracing B = blue)
Amnioinfusion can cause what changes in the fetal heart rate tracing?
An internal electronic fetal monitor tracing continues to record artifact despite equipment troubleshooting and replacement of the spiral electrode. The next action is to:
When fetal arterial blood pressure increases, the baroreceptors send impulses to the vagus nerve resulting in:
The black pattern represents the heart rate pattern for Baby A. The blue pattern represents the heart rate pattern for Baby B. A possible etiology of the baseline fetal heart rate of Baby A is:
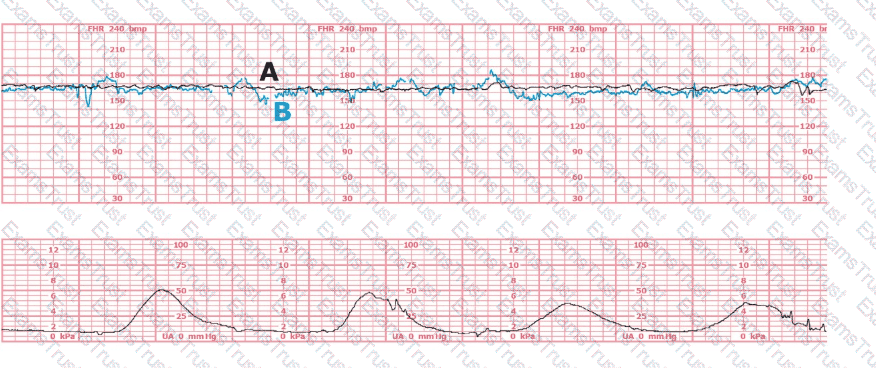
Based on the tracing shown, the first action should be to
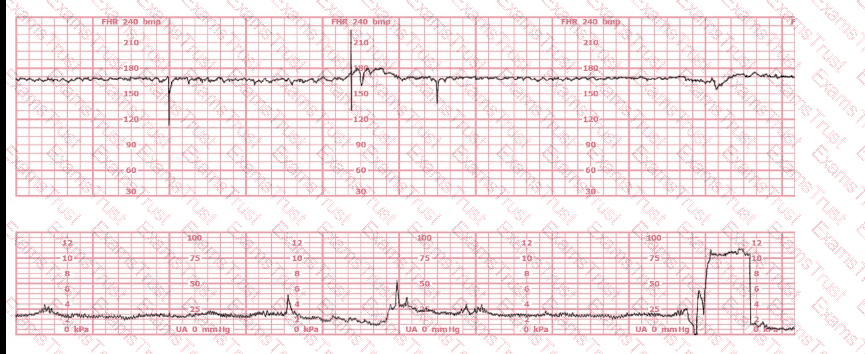
When R-R intervals are short, the fetal heart rate is
A key differentiating factor when determining if a deceleration is early or late is the
The main reason intrauterine pressure catheters are placed is to:
A 20-year-old woman (G1P0) at 40-weeks gestation was admitted for cervical ripening with dinoprostone (Cervidil) four hours ago. She developed the pattern shown one hour ago. She has been changed to a lateral position and given a fluid bolus, and the pattern continues. An appropriate intervention would be to:
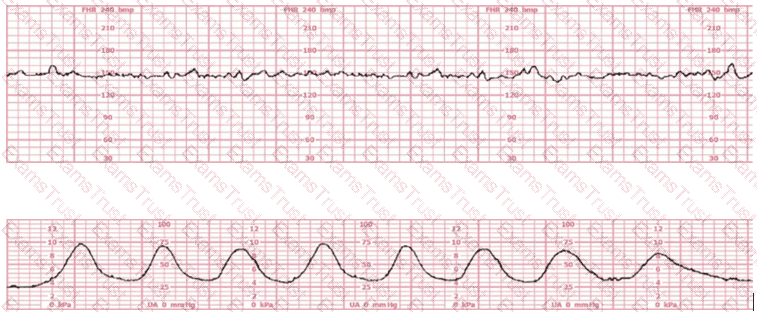
A woman experiences an eclamptic seizure during the second stage of labor. An anticipated fetal heart rate abnormality post-seizure would be:
Prenatal diagnosis shows that a fetus has renal agenesis. During delivery, what type of electronic fetal heart rate pattern is most likely to be seen due to a common complication associated with this syndrome?
(Full question statement)
This tracing is consistent with:
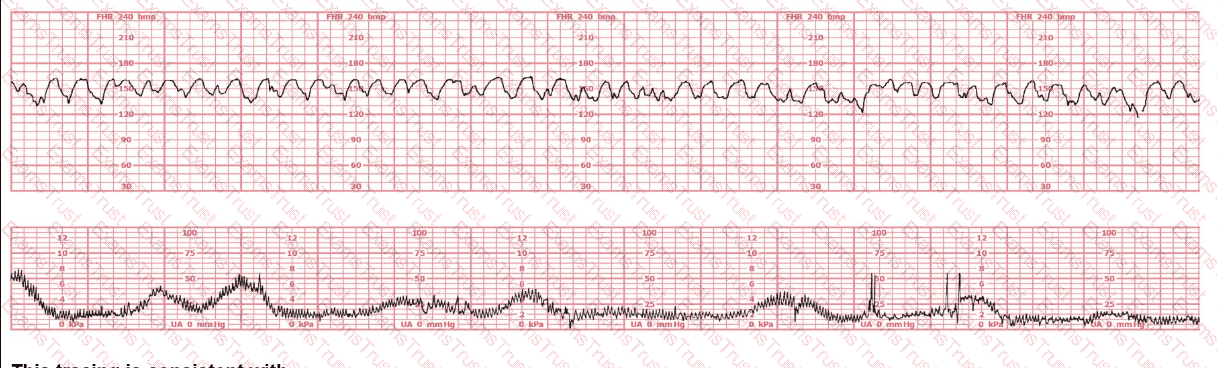
To differentiate a fetal dysrhythmia from artifact, it is important to recognize that artifact appears as deflections that are:
The most probable underlying fetal physiologic cause for this tracing would be:
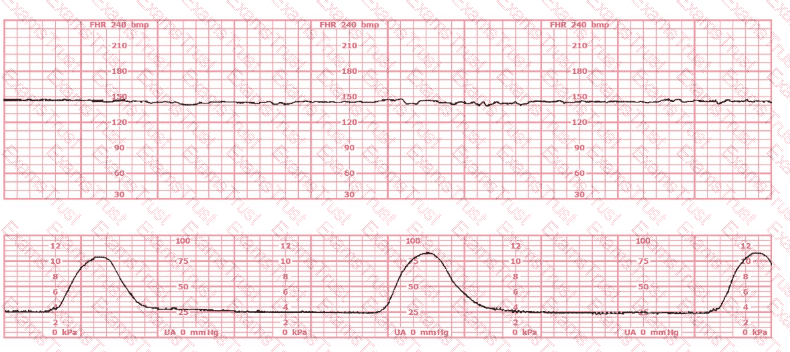
This patient received an epidural 15 minutes prior to the tracing shown. The next course of action is to:
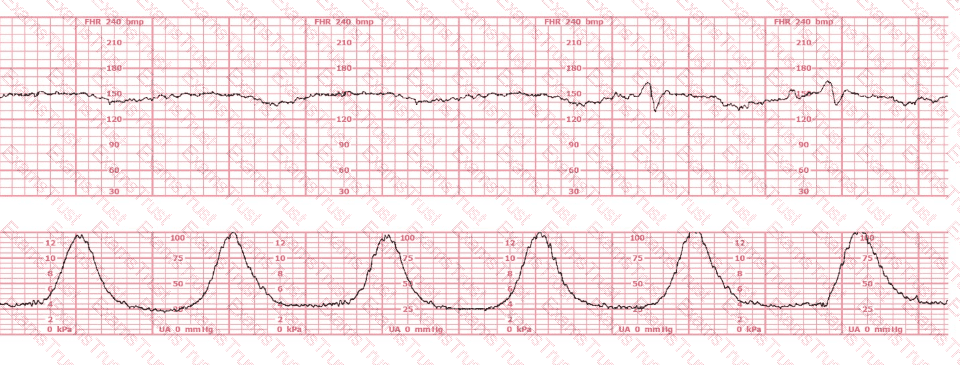
A woman reports 12 fetal movements over one hour. The best recommendation is to:
A patient at 41 weeks gestation is being induced. She has progressed slowly and is now at 6 cm, 90% effaced, –1 station. She has the fetal heart tracing shown despite repositioning. The next step in the management of this patient should be to:
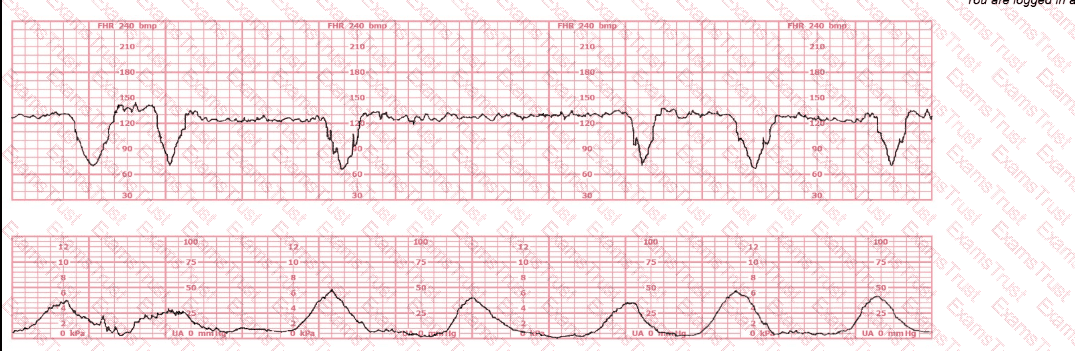
During the second stage of labor, a period of bradycardia develops. The fetal heart rate baseline variability is moderate. The most likely cause of this bradycardia is: