It is impossible to disable user “admin” at the menu “/user”
True
False
In MikroTik RouterOS, the default user “admin” is a special system account. While it can be renamed or assigned a new password, it cannot be disabled or removed from the /user menu. This account is always present and has full administrative rights unless manually restricted via group policy or firewall rules.
A.✔True – You cannot disable or delete the “admin” user account.
B.✘False – Disabling is not possible via normal means in /user.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – User Management Section:
"The default user 'admin' cannot be deleted or disabled. You may rename it or assign a strong password."
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Users and Access Control:
“The admin account is permanent. For security reasons, change its name or use a different account and firewall access.”
Extract from Terry Combs Notes – User Management:
“Admin is system-protected. You can change the username, but it cannot be disabled or removed.”
===========
A client that has successfully connected to a wireless network is considered to be which of the following? Choose all that apply:
Authenticated
Associated
Unauthenticated
Unassociated
For a client to exchange data over a wireless network, it must complete two key steps:
Association – Establishes the basic radio link between client and access point
Authentication – Verifies credentials (e.g., WPA2 handshake)
When both are complete, the client is both authenticated and associated.
A.✔Authenticated – Encryption and access control is complete
B.✔Associated – Wireless radio link is established
C.✘Unauthenticated – Incorrect; client is verified
D.✘Unassociated – Incorrect; client is linked to AP
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – Wireless Client States:
“A connected client is associated (Layer 2) and authenticated (security/credentials verified).”
Extract from Terry Combs MTCNA Notes – Wireless States:
“Authenticated and associated are required for data transfer. Unassociated = disconnected.”
===========
How many layers does the Open Systems Interconnection model have?
6
9
5
7
12
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a communication system into seven distinct layers. It is used to understand and design computer networking systems.
The seven layers of the OSI model are:
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
Each layer has its own specific purpose and interacts with adjacent layers to perform data transmission functions.
MTCNA Official Course Material – OSI Model Chapter:
“The OSI model consists of 7 layers. Understanding these layers is critical for troubleshooting and protocol analysis.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – OSI Model Section:
“There are exactly seven OSI layers. They range from the Physical Layer (Layer 1) to the Application Layer (Layer 7).”
Terry Combs Notes – OSI Summary Page:
“OSI = 7 Layers. The most important ones for network engineers are Layer 1 through Layer 4.”
Answer: DQUESTION NO: 13 [Routing]
How many usable IP addresses are there in a 20-bit subnet?
A. 4096
B. 4094
C. 2046
D. 2048
E. 2047
Answer: B
A /20 subnet means that 20 bits are used for the network portion, and 12 bits are left for host addresses. The total number of IP addresses available in such a subnet is:
2^12 = 4096 (total addresses)
Usable IP addresses = 4096 - 2 = 4094
→ (1 address is reserved for the network ID, and 1 for the broadcast address)
MTCNA Course Manual – Subnetting and IP Allocation:
“A subnet with n host bits gives 2^n total addresses. Always subtract 2 to account for network and broadcast addresses.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Subnet Calculations:
“/20 = 12 host bits → 4096 total IPs. Usable = 4094. Remember to subtract 2.”
Terry Combs MTCNA Notes – Addressing Math:
“20-bit subnet = 4094 usable IPs. Know how to compute 2^x and subtract 2.”
Answer: BQUESTION NO: 14 [Routing]
You have a router with configuration
Public IP: 202.168.125.45/24
Default gateway: 202.168.125.1
DNS server: 248.115.148.136, 248.115.148.137
Local IP: 192.168.2.1/24
Mark the correct configuration on client PC to access the Internet:
A. IP: 192.168.0.1/24, gateway: 192.168.2.1
B. IP: 192.168.2.253/24, gateway: 202.168.0.1
C. IP: 192.168.2.115/24, gateway: 192.168.2.1
D. IP: 192.168.2.2/24, gateway: 202.168.125.45
E. IP: 192.168.1.223/24, gateway: 248.115.148.136
Answer: C
To correctly configure a host in a private network behind a router:
The IP must match the local subnet (192.168.2.0/24)
The gateway must be the router’s local IP (192.168.2.1)
DNS settings can be default or custom, but IP and gateway must be valid
Let’s evaluate:
A. 192.168.0.1 → Wrong subnet (192.168.0.0/24 ≠ 192.168.2.0/24)❌
B. Gateway 202.168.0.1 → Invalid internal gateway❌
C. IP 192.168.2.115 with gateway 192.168.2.1 →✅Correct subnet and correct gateway
D. Gateway 202.168.125.45 → This is router’s public IP, not the correct gateway for LAN❌
E. IP 192.168.1.223 → Wrong subnet; also, gateway is DNS IP❌
MTCNA NAT Section – Network Configuration:
“Clients should be in the same subnet as the router’s local IP and must use that local IP as their gateway to reach outside networks.”
René Meneses Guide – Gateway and Addressing:
“The client’s IP should belong to the same subnet as the local router interface. Always verify gateway IP points to the internal address.”
Terry Combs Notes – Default Gateway Setup:
“The default gateway for local clients must be the internal router IP — not the public or DNS IP.”
Answer: CQUESTION NO: 15 [RouterBOARD Hardware]
Collisions are possible in full-duplex Ethernet networks:
A. true
B. false
Answer: B
In full-duplex Ethernet, devices can transmit and receive simultaneously on separate physical or logical channels. This eliminates the possibility of collisions because there is no need for devices to listen before transmitting — unlike half-duplex Ethernet, which uses CSMA/CD to manage potential collisions.
Full-duplex connections are the standard in modern switching environments and are always collision-free.
MTCNA Official Course Material – Ethernet & Duplex Modes:
“In full-duplex Ethernet, there are separate transmit and receive paths, and therefore, collisions cannot occur.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Ethernet Basics:
“Full-duplex = simultaneous send/receive = no collisions. Collisions are a legacy issue from half-duplex Ethernet.”
Terry Combs MTCNA Notes – CSMA/CD and Ethernet:
“Collision Detection (CD) is not used in full-duplex. Only half-duplex environments use CSMA/CD to manage access.”
What is the default protocol/port of (secure) winbox?
UDP/5678
TCP/22
TCP/8291
TCP/8080
Winbox is the graphical configuration utility for MikroTik routers. By default, Winbox connects to RouterOS over TCP port 8291.
A.✘UDP/5678 – Used for Winbox neighbor discovery, not for connecting.
B.✘TCP/22 – SSH service.
C.✔TCP/8291 – Default and official port for Winbox connections.
D.✘TCP/8080 – Often used for HTTP proxy; unrelated to Winbox.
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – RouterOS Access Methods:
“Winbox uses TCP port 8291 to establish connections to RouterOS.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Access Tools:
“Winbox connects via TCP 8291. Neighbor discovery uses UDP 5678.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – Winbox Port Info:
“TCP/8291 is the default port for Winbox. Ensure it is not blocked by firewall.”
It is possible to create a configuration where VLAN and PPTP interfaces are bridged together.
TRUE
FALSE
RouterOS allows different types of interfaces, including VLANs and PPP-based interfaces (like PPTP), to be added to a bridge. This creates a Layer 2 network between them, enabling transparent communication.
A.✔TRUE – Supported and commonly used in tunneling + VLAN transport.
B.✘FALSE – Incorrect.
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – Bridging Concepts:
“Bridging can include Ethernet, VLAN, wireless, and virtual interfaces such as PPTP and EOIP.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – Bridge Interface:
“Any Layer 2-capable interface (including VLANs, PPP tunnels, and Ethernet) can be included in a bridge.”
Extract from René Meneses Study Guide – Bridging and VLANs:
“It is possible to bridge VLAN interfaces with VPN interfaces for advanced Layer 2 tunneling scenarios.”
===========
Where is a hub specified in the OSI model?
Session layer
Physical layer
Data Link layer
Application layer
A hub is a simple Layer 1 (Physical Layer) device that does not understand MAC addresses or IP addresses. It simply repeats electrical signals to all connected ports without inspection or filtering.
MTCNA Course Material – OSI Layer Device Roles:
“Hubs operate at the Physical Layer. They do not process frames or packets and function purely as repeaters.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – OSI Devices:
“Hubs are Layer 1 devices. They send bits — not frames — and have no concept of MAC addresses.”
Other options:
A: Session layer is Layer 5, handles sessions between applications
C: Switches/bridges operate at the Data Link layer (Layer 2)
D: Application layer (Layer 7) is for user-level software like HTTP, FTP, etc.
Final Answer: BQUESTION NO: 138 [Cisco IOS – Access List Verification]
Which command is used to determine if an IP access list is enabled on a particular interface?
A. show access-lists
B. show interface
C. show ip interface
D. show interface access-lists
Answer: C
The command show ip interface displays the status of IP-level interface parameters, including whether an access list (ACL) is applied inbound or outbound.
Cisco IOS Command Reference – Interface ACL Check:
“Use show ip interface to verify whether an access list is applied to the interface and in which direction (in or out).”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Cisco Access List Monitoring:
“To verify ACL assignment to an interface, use show ip interface. It provides ACL status along with IP addressing info.”
Breakdown:
A: show access-lists → shows ACL contents, not interface bindings
B: show interface → shows interface stats, not ACL usage
D: Invalid syntax in Cisco IOS
Final Answer: CQUESTION NO: 139 [RouterOS Introduction – Transport Protocols]
Which protocol does DHCP use at the Transport layer?
A. IP
B. TCP
C. UDP
D. ARP
Answer: C
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) operates over UDP:
Client uses UDP port 68
Server uses UDP port 67
It is a connectionless protocol, and because clients typically do not yet have IP addresses, UDP is used due to its simplicity.
MTCNA Course Material – DHCP Protocol Layering:
“DHCP uses UDP for communication between clients and servers. TCP is not used due to the stateless, broadcast nature of DHCP discovery.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Port Assignments:
“UDP 67/68 are used by DHCP. TCP is not used because clients lack IPs initially.”
Other options:
A: IP is the network layer, not transport
B: TCP is used by reliable services (FTP, HTTP)
D: ARP resolves IP-to-MAC; unrelated to DHCP transport
Final Answer: CQUESTION NO: 140 [Cisco IOS – Remote Access Configuration]
Which of the following commands will allow you to set your Telnet password on a Cisco router?
A. line telnet 0 4
B. line aux 0 4
C. line vty 0 4
D. line con 0
Answer: C
The correct line configuration for remote Telnet (or SSH) access in Cisco IOS is via the virtual terminal (vty) lines. Typically, Cisco routers reserve 5 lines: vty 0 4. You then apply the password and login commands under this context.
Cisco IOS Configuration Guide – Telnet/VTY Setup:
“Use line vty 0 4 to configure access for Telnet sessions. Then use password and login to enforce authentication.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Cisco Access Configuration:
“VTY lines (virtual terminal) handle Telnet and SSH sessions. Console and aux lines are for local access.”
Other options:
A: line telnet is not a valid command
B: line aux → used for modem or auxiliary port access
D: line con 0 → used for console (local) access, not remote
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
What is necessary for PPPoE client configuration?
Interface (on which PPPoE client is going to work)
Static IP address on PPPoE client interface
ip firewall nat masquerade rule
To configure a PPPoE client on MikroTik, you need to:
Set the client interface (usually ether1 or another WAN-facing port).
Optionally add NAT masquerading to enable LAN users to reach the internet.
IP address on the interface is assigned dynamically from the ISP after PPPoE negotiation, so a static IP is not required.
Option Analysis:
A.✔Required – You must select the interface that initiates the PPPoE connection.
B.✘Not Required – The IP is typically assigned by the PPPoE server (ISP).
C.✔Required – NAT masquerade is commonly used to allow internet access for private IP clients behind the router.
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – PPPoE Client Setup:
“The PPPoE client must have an interface specified. A NAT masquerade rule is recommended for internet access sharing.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – PPPoE:
“You do not need to assign a static IP to the PPPoE client interface. IP is received after successful login.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – PPPoE Client:
“After setting up the interface and credentials, PPPoE client negotiates and receives dynamic IP. Add NAT if routing LAN traffic.”
===========
Is it possible to limit how many clients are able to connect to an access point?
No it's not possible at all
Yes, but only with access-lists
Yes
Yes, MikroTik RouterOS allows administrators to limit the maximum number of clients that can connect to a wireless access point. This can be done through the wireless interface settings using the max-station-count parameter.
The max-station-count option defines the maximum number of client devices (stations) that may be connected simultaneously. You are not restricted to access-lists; this setting works globally per interface.
A.❌Incorrect. It is definitely possible.
B.❌Limiting via access-list is one method (e.g., per MAC), but the more general and scalable method is via max-station-count.
C.✅Correct. MikroTik provides both general limits and fine control (like access-lists or registration-table rules).
MTCNA Official Wireless Module – Access Point Configuration:
“Set the maximum number of stations using max-station-count. This is a hardware-level control on the interface.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Wireless Configuration:
“Limiting clients can be done through access-lists or via interface properties such as max-station-count.”
Terry Combs Notes – Wireless Station Limits:
“Use max-station-count under wireless settings. This applies a hard limit on how many clients can connect.”
Answer: CQUESTION NO: 29 [QoS – Simple Queues]
The highest queue priority is:
A. 1
B. 256
C. 16
D. 8
Answer: A
MikroTik RouterOS supports prioritizing traffic in queues using a numerical priority system. The queue priority values range from 1 to 8, where:
1 = Highest priority (most preferred)
8 = Lowest priority (least preferred)
This means that traffic marked with priority 1 is processed before traffic with lower priorities. Priorities are used within simple queues, queue trees, and in some packet marking strategies.
Evaluation:
A. 1 →✅Correct. This is the highest priority.
B. 256 →❌Invalid priority value in MikroTik queues.
C. 16 →❌Priority range is only 1 to 8.
D. 8 →❌Lowest priority.
MTCNA Course Slides – QoS and Queuing:
“Queue priority values range from 1 to 8. Lower values indicate higher priority.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Traffic Management Section:
“MikroTik queues use priority values from 1 (highest) to 8 (lowest).”
Terry Combs Notes – QoS and Prioritization:
“Set queue priority to 1 for critical traffic like VoIP or routing protocols.”
Answer: AQUESTION NO: 30 [QoS – Simple Queues]
How many different priorities can be selected for queues in MikroTik RouterOS?
A. 16
B. 1
C. 8
D. 0
Answer: C
MikroTik RouterOS allows you to assign one of 8 different priority levels to each queue. These range from 1 (highest) to 8 (lowest). This allows for traffic shaping and prioritization in simple queues and queue trees.
These priority levels are used when multiple queues are competing for bandwidth or processing time. They influence which traffic gets handled first when congestion occurs.
A. 16 →❌Invalid. Only 8 supported.
B. 1 →❌Not correct. Only says one value; MikroTik supports multiple.
C. 8 →✅Correct. There are 8 valid priority values.
D. 0 →❌Priority 0 is not valid in MikroTik queues.
MTCNA Course Manual – Queues and Priorities:
“MikroTik queues support 8 priority levels (1–8). These affect which traffic is processed first.”
René Meneses Study Guide – QoS Mechanics:
“You can select between 8 priorities. These are configured per queue to define traffic importance.”
Terry Combs Notes – Simple Queues:
“Only 8 priority values exist. They follow a numerical scale from 1 to 8, not 0 or beyond.”
What protocol is used for Ping and Trace route?
DHCP
IP
TCP
ICMP – ping
UDP – trace route
Both ping and traceroute are diagnostic tools used to test connectivity and network path behavior. While both use IP as the transport layer, they rely on specific protocols:
Ping uses ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply messages.
Traceroute typically uses UDP packets with increasing TTL (Time-To-Live) values to discover each hop.
On MikroTik devices, ping uses ICMP and traceroute uses UDP by default (though ICMP traceroute is also available in some implementations).
A. DHCP is unrelated. It's a protocol for IP address assignment.
B. IP is a network-layer protocol underlying ICMP and UDP, but it's not the specific diagnostic protocol.
C. TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, not used for ping/traceroute.
D. Correct. ICMP is the protocol behind ping.
E. Correct. UDP is used by default in traceroute to trigger ICMP Time Exceeded messages from routers.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – Tools Section:
“Ping uses the ICMP protocol to send Echo Request and receive Echo Reply. Traceroute sends UDP packets with incremented TTL values to discover intermediate hops.”
Extract from René Meneses Study Guide – Diagnostic Tools:
"Traceroute in RouterOS sends UDP packets to a random port. Routers that receive the packet send ICMP Time Exceeded messages back when TTL expires. Ping uses ICMP directly."
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – Ping and Traceroute:
“Ping uses ICMP protocol. Traceroute sends UDP packets, increasing TTL by one for each hop.”
What is the default TTL (time to live) on a router that an IP packet can experience before it will be discarded?
60
30
1
64
TTL (Time to Live) is a field in the IP header that limits the number of hops a packet can travel. Each router that processes the packet decrements the TTL by 1. When TTL reaches 0, the packet is dropped.
Default TTL values vary by operating system, but in RouterOS and many Linux-based systems, the default TTL is 64.
A. 60 → Incorrect, used in some systems but not the MikroTik default
B. 30 → Incorrect
C. 1 → Incorrect; would allow only one hop
D. 64 →✔Correct
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – TTL Field Explanation:
"The default TTL in RouterOS and most Unix-like systems is 64. Each router decrements this by 1 until the packet is discarded."
Extract from René Meneses Study Guide – IP Protocol Details:
“TTL is initialized to 64 by default in MikroTik RouterOS.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – IP Protocol Section:
"RouterOS sets default TTL of 64 unless manually configured otherwise."
===========
What flavor of Network Address Translation can be used to have one IP address allow many users to connect to the global Internet?
NAT
Static
Dynamic
PAT
PAT (Port Address Translation) is a subtype of NAT that maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address using different port numbers. It is the most common form of NAT used in home and business networks to allow multiple internal hosts to access the internet using one public IP address.
MTCNA Course Material – NAT Concepts:
“PAT (also known as NAT overload) allows multiple devices to share a single public IP address. It uses different port numbers to distinguish sessions.”
Cisco IOS NAT Configuration Guide:
“PAT translates multiple local IP addresses to one public IP address by assigning different port numbers to each session.”
Other options:
A: Generic term — not specific enough
B: Static NAT maps one private IP to one public IP
C: Dynamic NAT maps private IPs to a pool of public IPs, not one-to-many
Final Answer: DQUESTION NO: 149 [IPv6 – Addressing Standards]
How long is an IPv6 address?
A. 32 bits
B. 128 bytes
C. 64 bits
D. 128 bits
Answer: D
IPv6 addresses are 128 bits in length, represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334). This allows for a vastly larger address space compared to IPv4 (32 bits).
MTCNA Course Material – IPv6 Basics:
“An IPv6 address is 128 bits long, providing 3.4×10^38 possible addresses. It is written in hexadecimal format.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – IPv6 Addressing:
“IPv6 = 128 bits, not bytes. Address includes a 64-bit network prefix and 64-bit interface identifier.”
Other options:
A: 32 bits is IPv4
B: 128 bytes = 1024 bits — incorrect
C: 64 bits = only half of an IPv6 address
Final Answer: DQUESTION NO: 150 [IP Addressing – Subnetting]
How many usable IP addresses are there in a 23-bit (255.255.254.0) subnet?
A. 512
B. 510
C. 508
D. 254
Answer: B
A /23 subnet provides 2^9 = 512 total addresses.
Subtract 2 (network address + broadcast address)
512 – 2 = 510 usable IP addresses
MTCNA Course Material – Subnet Calculations:
“For any subnet, usable hosts = 2^(32 – subnet mask bits) – 2.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – IP Subnetting:
“/23 provides 512 total addresses; usable = 510 after subtracting network and broadcast.”
Option Breakdown:
A: Total addresses (512)
B:✔Usable addresses (510)
C: Incorrect (508 is for /23 minus 4 — not relevant here)
D: 254 is usable for /24
When backing up your router by using the ‘Export’ command, the following happens:
Winbox usernames and passwords are backed up
The Export file can be edited with a standard text editor after its creation
You are requested to give the export file a name
MikroTik RouterOS supports two types of configuration backups:
/export – creates a human-readable script (.rsc file) containing configuration commands. This file can be edited using any text editor and later imported into another device.
/system backup – creates a binary image including all settings, passwords, and sensitive data.
Option analysis:
A.✘Incorrect–Export does NOT include passwords or Winbox credentials for security reasons
B.✔Correct–Exported .rsc files are plain-text and editable
C.✘Incorrect–The export file is automatically named (e.g., export.rsc) unless redirected manually
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – Backup vs Export:
"Export is a plain-text script file that can be edited and reused. It does not contain encrypted passwords or user credentials."
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Backup and Restore:
“Use export to create editable configurations. It excludes sensitive data like passwords.”
Extract from Terry Combs Notes – Configuration Export:
“Export is readable, editable, and ideal for replicating setups. Passwords and some private info are excluded.”
===========
What does this simple queue do (check the image)?
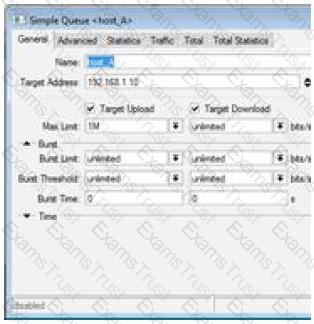
The screenshot shows a Simple Queue named "host_A" with:
Target Address: 192.168.1.10
Target Upload: Checked
Target Download: Checked
Max Limit: 1M (upload), unlimited (download)
Queue guarantees upload data rate of one megabit per second for host 192.168.1.10
Queue limits host 192.168.1.10 download data rate to one megabit per second.
Queue limits host 192.168.1.10 upload data rate to one megabit per second.
Queue guarantees download data rate of one megabit per second for host 192.168.1.10
The “Max Limit” value in MikroTik Simple Queues defines the maximum allowed bandwidth. In this case:
Target Address: 192.168.1.10
Target Upload = 1M → The host can upload at a maximum of 1 Mbps
Target Download = unlimited → No restriction on download
This does not “guarantee” bandwidth — it enforces a ceiling. A guaranteed rate would require "Limit-at" to be set.
Evaluation:
A.❌This queue limits, it does not guarantee a minimum bandwidth.
B.❌Download is set to unlimited — no limitation.
C.✅Upload is limited to 1 Mbps — correct.
D.❌Download rate is unlimited — no guarantee or limit.
MTCNA Course Manual – Simple Queue Explanation:
“Max-limit sets the maximum throughput for upload/download. It’s a ceiling, not a guarantee.”
René Meneses Guide – Simple Queues Explained:
“In this case, upload is capped at 1M. No burst or download limit is applied.”
Terry Combs Notes – Queue Properties:
“Always distinguish between 'limit-at' (minimum guarantee) and 'max-limit' (maximum cap).”
It is possible to create an encrypted PPPoE tunnel in RouterOS:
True
False
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) does not natively support encryption. It provides authentication using PAP/CHAP and allows IP assignment, but any data transmitted through a PPPoE tunnel is unencrypted unless another encryption mechanism (such as IPSec) is used on top of it.
MikroTik RouterOS supports encrypted tunneling protocols such as SSTP, L2TP/IPSec, or OpenVPN, but not native encryption in PPPoE.
MTCNA Course Manual – PPP Protocols Overview:
“PPPoE supports user authentication and compression but not encryption by itself.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Tunneling Protocols:
“PPPoE is not secure by design. If encryption is needed, use SSTP or L2TP/IPSec.”
Terry Combs Notes – PPP Protocol Capabilities:
“PPPoE does not encrypt data. Only authentication is handled within PPP.”
Answer: BQUESTION NO: 36 [Wireless]
Why is it useful to set a Radio Name on the radio interface?
A. To identify a station in the Access List
B. To identify a station in Neighbor discovery
C. To identify a station in a list of connected clients
Answer: C
Setting a Radio Name in RouterOS provides a unique identifier that is visible to other devices in the wireless environment. It is particularly helpful for identifying connected clients in the registration table on the Access Point.
This name does not affect Access List matching or general Layer 2 communication — it’s used for human readability and monitoring.
A. Access List uses MAC addresses for filtering →❌
B. Neighbor discovery identifies devices based on MAC, IP, and identity →❌
C. Correct → Radio Name shows up in the registration table and helps identify stations✅
MTCNA Wireless Module – Interface Settings:
“The Radio Name is shown in the registration table of access points, making it easier to identify connected clients.”
René Meneses Guide – Wireless Management Tips:
“Use Radio Names to label devices in multi-client setups. It appears under registration when clients connect.”
Terry Combs Notes – Wireless Interface Options:
“Radio Name is not used for access filtering — it’s for display and diagnostics.”
Answer: CQUESTION NO: 37 [DHCP]
A DHCP server is configured on a LAN interface which is a port on a bridge. The DHCP server does not start. What could be the reason(s)?
A. The DHCP server cannot run on an interface which is also a bridge port
B. There might not be an IP address assigned to the LAN Interface
C. The IP address pool could be incorrectly defined
D. There may be multiple IP addresses set on the LAN interface
Answer: B, C
For a DHCP server to operate properly, the following conditions must be met:
The DHCP server must be attached to the correct interface (typically the bridge, not individual ports).
The bridge interface must have a valid IP address.
The IP address pool must be defined correctly (matching subnet, avoiding conflicts).
Let’s evaluate:
A.❌Incorrect. DHCP can run on a bridge or an interface on a bridge. It is recommended to attach DHCP to the bridge, not individual ports.
B.✅Correct. If there is no IP address on the interface (bridge), DHCP won’t start.
C.✅Correct. If the address pool is misconfigured (e.g., outside the subnet or overlapping with the router’s IP), DHCP won’t function.
D.❌Not a valid blocker. Multiple IPs can exist on the interface; DHCP still works if one is valid.
MTCNA DHCP Module – Configuration Troubleshooting:
“Make sure that the interface (bridge) where the DHCP server is assigned has a valid IP and a properly defined pool.”
René Meneses Guide – DHCP Server Setup:
“DHCP will not function if no IP is assigned to the interface. Check the pool range and binding address.”
Terry Combs Notes – DHCP Tips:
“Assign the DHCP server to the bridge, not individual ports. Missing IP or incorrect pool = DHCP won’t start.”
Answer: B, CQUESTION NO: 38 [PPP]
There can be more than one PPPoE server in a single broadcast domain:
A. True
B. False
Answer: A
Yes, it is possible — and fully supported — to run multiple PPPoE servers in the same Layer 2 broadcast domain. Clients will receive Offer packets (PADO) from all PPPoE servers, and can choose which one to connect to based on configuration or server name (service name).
This is commonly used in ISP networks to provide redundancy or offer different service types.
MTCNA Course Manual – PPPoE Deployment:
“Multiple PPPoE servers may exist in the same Layer 2 domain. Clients choose based on response or service name.”
René Meneses Study Guide – PPPoE Operations:
“PPPoE discovery protocol supports multi-server environments. Clients may be configured to select a preferred one.”
Terry Combs Notes – PPPoE Server Design:
“Several PPPoE servers can coexist. Just avoid assigning overlapping IP pools.”
You have a DHCP server on your MikroTik router. The IP addresses 10.1.2.2–10.2.2.20 are distributed in the DHCP network. Additionally, 3 static IP addresses are defined for your servers: 10.1.2.31–10.1.2.33.
After a while, 20 more IP addresses need to be distributed in the network. It is possible to distribute the extra IP addresses without adding another DHCP Server:
True
False
MikroTik RouterOS allows DHCP administrators to modify the DHCP address pool without creating an additional DHCP server. You can simply edit or extend the address pool range, and the DHCP server will start offering those new IPs.
Therefore, it is completely possible to:
Extend the existing address pool
Exclude statically assigned IPs
Continue using the same DHCP Server instance
You do NOT need to create a second DHCP server on the same interface.
MTCNA Course Manual – DHCP Configuration:
“It is possible to expand the address-pool dynamically without adding additional DHCP servers. Just add more IPs to the pool.”
René Meneses Study Guide – DHCP Pools Section:
“You can edit the address pool associated with the DHCP server anytime to include more addresses. No need to create another server.”
Terry Combs Notes – DHCP Tips:
“Keep one DHCP server per subnet. Extend pools via IP > Pool if more IPs are needed.”
Answer: AQUESTION NO: 25 [Wireless]
In which order are the entries in Access List and Connect List processed?
A. By Signal Strength Range
B. By interface name
C. In sequence order
D. In a random order
Answer: C
MikroTik processes the entries in the Access List and Connect List in a top-down fashion —meaning that the first matching entry is the one applied. This is known as sequence order (from top to bottom).
Each rule is checked in the order it appears in the list, and once a match is found, the rest of the list is ignored for that client.
Incorrect options:
A. Signal strength is only a condition, not a sorting method
B. Interface names are part of rule conditions
D. Not random — rules are processed sequentially
MTCNA Official Training Manual – Wireless Access & Connect List:
“Rules in access-list and connect-list are checked in the order they are listed. Once a match is found, further rules are ignored.”
René Meneses Guide – Wireless Access Rules:
“Access-list is evaluated top-down. Sequence matters.”
Terry Combs MTCNA Notes – Wireless Filtering:
“Be careful with order. The first matching rule is applied — no exceptions.”
Answer: CQUESTION NO: 26 [Wireless]
During a scan, in order to see all the available wireless frequencies that are supported by the card, the following option must be selected in the wireless card's "Frequency Mode":
A. superchannel
B. regulatory domain
C. manual txpower
Answer: A
In MikroTik RouterOS, enabling the "superchannel" frequency mode allows access to all frequencies supported by the wireless chip, including those that may be outside of country-specific regulatory limits. This mode is typically used in lab testing or in regions where regulations permit.
A. superchannel →✅Correct. Enables full frequency range
B. regulatory domain → Restricts visible frequencies to region’s law
C. manual txpower → Controls power output, not frequency scanning
MTCNA Course Material – Wireless Configuration Options:
“To unlock all available wireless frequencies for scanning or connection, enable the 'superchannel' frequency mode.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Wireless Advanced Config:
“Superchannel mode shows all channels supported by the hardware. Use with caution — may violate regulations.”
Terry Combs Notes – Wireless Modes:
“Want to see hidden or extended frequencies? Use superchannel mode. Not legal in every region.”
Answer: AQUESTION NO: 27 [NAT]
It is required to make a web server on a private LAN visible on the public internet. Only the web server port should be visible to the public. Which of the following configuration steps must be met? (Select all that apply)
A. Public IP address of the web server must be installed on the NAT Router
B. In IP firewall NAT, there should be a dst-nat between the public IP of the router and the private IP of the web server
C. Connection Tracking must be enabled on NAT router
D. A route between the NAT router and the web server must exist
E. LAN address of the web server should be routable on the internet
Answer: B, C, D
To expose a web server behind a MikroTik router to the public, the following steps must be met:
B. dst-nat rule must be created to forward incoming requests (e.g., TCP port 80) to the internal web server IP →✅Required
C. Connection Tracking must be enabled, otherwise NAT rules won’t function →✅Required
D. A route between the NAT router and the web server must exist (usually a directly connected subnet) →✅Required
Incorrect Options:
A. The public IP does not need to be installed on the web server — it remains private →❌
E. Private LAN IP (like 192.168.x.x) does not need to be routable on the internet →❌
MTCNA Course Manual – NAT and Port Forwarding Section:
“To expose internal services to the public internet, use dst-nat. Ensure connection tracking is active and the server is reachable through routing.”
René Meneses Guide – NAT Configuration:
“DST-NAT forwards specific ports to internal IPs. Connection tracking is a prerequisite. LAN IPs remain private.”
Terry Combs Notes – Web Server NAT Rules:
“No need to assign public IP to server. Just configure a proper NAT rule and ensure routing exists internally.”
════════════════════════════════════════════
Domain Name System (DNS) requests can use protocol/port:
UDP
TCP port 53
DNS primarily uses UDP port 53 for most query/response operations. However, TCP port 53 is also used, particularly for larger responses (such as DNS zone transfers or DNSSEC).
A.✔UDP – Used for standard DNS queries due to lower overhead.
B.✔TCP port 53 – Used when UDP is insufficient, especially for zone transfers (AXFR/IXFR).
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – DNS and Networking Services:
“DNS typically uses UDP/53, but falls back to TCP/53 for larger queries or zone transfers.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – DNS Settings:
“DNS uses UDP for general queries. TCP is used when UDP cannot accommodate the size of the response.”
===========
Which default route will be active?
/ip route
add disabled=no distance=10 dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=1.1.1.1
add disabled=no distance=5 dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=2.2.2.2
Route via gateway 2.2.2.2
Route via gateway 1.1.1.1
In MikroTik RouterOS (and in routing in general), the "distance" value determines the priority of a route. The route with the lowest distance will be preferred.
Here:
Route to 0.0.0.0/0 via 1.1.1.1 has distance = 10
Route to 0.0.0.0/0 via 2.2.2.2 has distance = 5 → lower, so preferred✅
Unless the lower-distance route is invalid or unreachable, it will always be selected.
MTCNA Course Manual – Static Routing:
“The lower the distance value, the higher the route’s priority. Routes are selected based on administrative distance first.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Route Distance:
“A route with distance 1 is preferred over a route with distance 2. It does not matter which was added first.”
Terry Combs Notes – Routing Behavior:
“RouterOS evaluates the distance (priority) before anything else. Smallest value wins.”
Answer: AQUESTION NO: 44 [Firewall]
What does the firewall action "Redirect" do? Select all true statements.
A. Redirects a packet to a specified port on the router
B. Redirects a packet to a specified IP
C. Redirects a packet to the router
D. Redirects a packet to a specified port on a host in the network
Answer: A, C
The redirect action in MikroTik’s NAT firewall rules is used to force traffic (usually from LAN clients) to a local service on the router — for example, redirecting all DNS queries to the router’s DNS server, or forcing web traffic to a proxy.
Details:
It changes the destination IP to the router's IP automatically (without needing to specify it)
It also allows port redirection (e.g., dst-port=80 → to 3128 for proxy)
Evaluation:
A.✅True — You can redirect to a specific port on the router
B.❌False — Redirect does not change destination IP to an arbitrary host; for that, use dst-nat
C.✅True — Redirect forces traffic to the router itself
D.❌False — dst-nat is used to forward packets to internal hosts, not redirect
MTCNA Course Manual – NAT Actions:
“Redirect action changes destination to the router itself. This is useful for forcing traffic through router services.”
René Meneses Guide – NAT Behavior:
“Redirect = router-local services like DNS or proxy. Use dst-nat for remote hosts.”
Terry Combs Notes – Firewall Actions:
“Use redirect when you want to intercept traffic and handle it locally on the router.”
Answer: A, CQUESTION NO: 45 [PPP / Tunnels]
Which port does PPTP use by default?
A. TCP 1721
B. UDP 1723
C. TCP 1723
D. UDP 1721
Answer: C
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) uses:
TCP port 1723 for control and session initiation
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) protocol (protocol number 47) for tunneling
No UDP port is used by PPTP.
Evaluation:
A. TCP 1721 →❌Invalid port
B. UDP 1723 →❌Incorrect protocol (TCP is used, not UDP)
C.✅TCP 1723 → Correct
D.❌Invalid (wrong protocol and port)
MTCNA Tunneling Section – PPTP Overview:
“PPTP uses TCP port 1723 for control and GRE protocol for tunneling traffic.”
René Meneses MTCNA Guide – PPTP Characteristics:
“PPTP = TCP/1723 + GRE (not a port, but a protocol). Allow both on firewall.”
Terry Combs Notes – VPN Protocol Reference:
“PPTP: TCP 1723. GRE must be permitted for tunnel data.”
Answer: CQUESTION NO: 46 [Firewall]
Which firewall chain should you use to filter ICMP packets from the router itself?
A. input
B. postrouting
C. forward
D. output
Answer: D
MikroTik RouterOS uses firewall chains to process packets based on direction:
input: For packets destined to the router itself (from outside)
output: For packets originating from the router (e.g., router pings)
forward: For packets passing through the router between interfaces
postrouting: Used for NAT and marking, not filtering
Therefore:
To block/allow ICMP (ping) generated by the router (e.g., netwatch, DNS probes), use the output chain
To block incoming pings to the router, use input
To block pings between LAN and WAN, use forward
MTCNA Firewall Module – Chain Responsibilities:
“To control traffic originating from the router itself, use the output chain. For example, when the router itself sends ICMP requests.”
René Meneses Guide – Firewall Chains Explained:
“output is for locally generated traffic. input is for inbound traffic to the router.”
Terry Combs Notes – Chain Use Cases:
“Ping from router = output. Ping to router = input. Ping between networks = forward.”
Action=redirect applies to
Firewall Filter rules
DST-NAT rules
Route rules
SRC-NAT rules
The redirect action is a specialized type of destination NAT (dst-nat) used to force traffic to a local port on the router (typically for transparent proxies or redirection to hotspot portals). This action is only valid in DST-NAT rules and does not apply to firewall filters, routing rules, or source NAT.
Option breakdown:
A.✘Firewall Filter – These rules allow, drop, or reject traffic, not perform redirection.
B.✔DST-NAT – Redirect is a valid dst-nat action and is processed in the prerouting chain.
C.✘Route – Routing rules do not include NAT actions.
D.✘SRC-NAT – Used for source address translation, not redirection.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – NAT Table & Actions:
“Redirect is an action under dst-nat. It rewrites destination address to the router itself, used for web proxy or hotspot.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – NAT Types:
“Use action=redirect in dst-nat rules to direct traffic to local services like proxy or DNS.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – NAT Rule Actions:
“redirect: redirects packet to local router port. Can only be used in dst-nat chain.”
===========
The correct order for PPPoE discovery stage is:
Initialization, Session confirmation, Request and Offer
Initialization, Offer, Request and Session confirmation
Request, Initialization, Session confirmation and Offer
Request, Offer, Initialization and Session confirmation
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) uses a discovery stage before establishing the actual PPP session. The correct sequence is:
Initialization → Client sends a PADI (PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation)
Offer → Server responds with PADO (PPPoE Active Discovery Offer)
Request → Client sends PADR (PPPoE Active Discovery Request)
Session Confirmation → Server sends PADS (PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation)
A.✘Wrong sequence
B.✔Correct – Matches the technical flow: PADI → PADO → PADR → PADS
C.✘Incorrect order
D.✘Incorrect order
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – PPPoE Process:
“The PPPoE discovery stage includes PADI, PADO, PADR, and PADS messages. This translates to Initialization, Offer, Request, Session confirmation.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – PPPoE Protocol:
“The discovery stage is used to establish a PPPoE session and includes four steps: PADI, PADO, PADR, and PADS.”
===========
What wireless card can we use to achieve 100 Mbps actual wireless throughput?
802.11 b/g
802.11 a/b/g
802.11 a
802.11 a/n
802.11 a/b/g/n
To achieve actual throughput of 100 Mbps, you must use 802.11n, which supports higher data rates through technologies such as MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) and channel bonding. 802.11n provides theoretical speeds up to 150 Mbps per stream and actual throughput above 100 Mbps under good conditions.
802.11a/b/g maxes out around 20–25 Mbps real throughput
802.11n (especially in 5 GHz band via 802.11a/n) is required to exceed 100 Mbps actual throughput
MTCNA Course Material – Wireless Standards and Data Rates:
“802.11n with proper channel width and MIMO can achieve over 100 Mbps of real throughput.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Wireless Performance:
“Only 802.11n can reach 100+ Mbps in practical use. Legacy modes (a/b/g) fall short due to modulation limits.”
Breakdown:
A/B/C: Do not support 100 Mbps throughput
D:✔802.11a/n supports 100+ Mbps
E: While also valid, D is more precise for the specific requirement (focused on a/n only)
Final Answer: DQUESTION NO: 156 [Firewall – Mangle Chains]
It is possible to add user-defined chains in ip firewall mangle.
A. True
B. False
Answer: A
RouterOS allows users to define custom chains in the mangle table, giving more flexibility for organizing and managing rules. This is particularly useful in complex routing and QoS configurations.
MikroTik Wiki – Firewall Mangle:
“Custom chains can be created using the add chain=your_chain_name command. Then you can jump to them from built-in chains.”
MTCNA Course Material – Mangle & Packet Flow:
“User-defined chains help separate logic and simplify processing. You can jump into them from prerouting, forward, or postrouting.”
Final Answer: AQUESTION NO: 157 [Firewall – NAT and Redirect Actions]
Action=redirect allows you to make:
A. Transparent DNS Cache
B. Forward DNS to another device IP address
C. Enable Local Service
D. Transparent HTTP Proxy
Answer: D
In RouterOS, action=redirect is used in NAT rules to redirect traffic destined for specific ports to local services. This is often used for:
Transparent web proxy (redirect port 80 to a local proxy service)
Transparent DNS interception (if RouterOS is the DNS server)
In most practical MikroTik use cases, redirect is associated with Transparent HTTP Proxy.
MTCNA Course Material – NAT Configuration:
“action=redirect rewrites the destination address to the router’s own IP. It is commonly used to create transparent web proxies.”
MikroTik Wiki – NAT Redirect:
“Redirect is used for redirecting traffic to local services like web proxy or DNS cache on the router.”
Breakdown:
A: Possible, but limited use; DNS cache works better with dst-nat
B: Incorrect — to forward to another IP, use dst-nat
C: Misleading — enabling local services doesn't require redirect
D:✔Correct—redirect enables transparent proxy setup
Final Answer: DQUESTION NO: 158 [Routing – Automatically Created Routes]
What letters appear next to a route, which is automatically created by RouterOS when user adds a valid address to an active interface?
A. I
B. D
C. A
D. S
E. C
Answer: E
In RouterOS, when an IP address is assigned to an interface, a connected route is automatically created. These routes are marked with the letter “C” in the routing table, denoting “Connected.”
MikroTik Wiki – Routing Table Flags:
“C – directly connected routes (assigned via /ip address), added automatically when interface is active.”
MTCNA Course Material – Static vs Dynamic Routes:
“Connected (C) routes are added automatically when IP is assigned to an interface.”
Flag meanings:
C:✔Connected
S: Static
D: Dynamic
A: Active (not a route type)
I: Invalid or intermediate (not shown for connected)
Is action=masquerade allowed in chain=dstnat?
yes, but only if dst-addr is specified
yes
yes, but it works only for incoming connections
no
The action=masquerade is used exclusively in the srcnat chain. It dynamically hides internal IP addresses behind the router's public IP. It cannot be used in the dstnat chain.
A.✘Incorrect – masquerade is not allowed in dstnat regardless of parameters.
B.✘Incorrect – masquerade is not valid in the dstnat chain.
C.✘Incorrect – masquerade does not operate in dstnat, direction does not change this.
D.✔Correct – masquerade must only be used in chain=srcnat.
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – NAT Concepts:
“Masquerade is a special type of source NAT used only in the srcnat chain. It is invalid in dstnat.”
Extract from René Meneses Study Guide – NAT Actions:
“Use action=masquerade in chain=srcnat. RouterOS will not accept it in dstnat.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – NAT Rules:
“action=masquerade is not allowed in dstnat chain and will result in error if applied.”
===========
You cannot use OSPF and RIP routing protocols simultaneously on RouterOS.
FALSE
TRUE
MikroTik RouterOS supports running multiple dynamic routing protocols simultaneously, including RIP, OSPF, and BGP. They are independent processes and can be configured in parallel. This is commonly used in complex network environments or during routing migrations.
A.✔FALSE – You can run OSPF and RIP at the same time.
B.✘TRUE – Incorrect; both protocols are fully supported to coexist.
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – Dynamic Routing:
“RouterOS supports multiple dynamic routing protocols, including simultaneous use of RIP and OSPF.”
Extract from René Meneses Study Guide – Routing Protocols:
“You can configure both RIP and OSPF to run at the same time on a single router.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – Routing Overview:
“RouterOS allows multiple routing protocols to operate concurrently.”
===========
How long is level 1 (demo) license valid?
24 hours
Infinite time
1 month
1 year
RouterOS Level 1 license is the demo license that comes with all RouterOS installations (particularly on x86 or CHR before activation). It is unrestricted in time, meaning it never expires, but functionality is extremely limited.
A. 24 hours → Incorrect. There is no such time-limited restriction.
B. Infinite time → Correct. Level 1 license is perpetual but has limited features.
C. 1 month → Incorrect. MikroTik does not impose monthly timeouts on license levels.
D. 1 year → Incorrect. No temporary time-bound license is assigned by default.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – Licensing Section:
“Level 1 (demo) license is unlimited in time but has very limited functionality. It is designed for testing purposes only.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – RouterOS Licensing:
“The Level 1 license is not time-limited, but it cannot be used in production due to its lack of key features.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – Licensing Model:
“License level 1 is a free demo license that does not expire.”
===========
How many IP addresses can one find in the header of an IP packet?
4
2
3
1
An IP packet contains two critical IP addresses in its header:
Source IP address – the IP of the sending host
Destination IP address – the IP of the receiving host
These addresses allow routers to forward the packet from source to destination over Layer 3 (Network Layer).
Other values in the IP header include TTL, protocol type, and checksum — but not additional IP addresses.
A. 4 →❌Incorrect. Only 2 IPs are included
B. 2 →✅Correct: Source and Destination
C. 3 →❌Some protocols like NAT may temporarily associate more addresses, but not in header
D. 1 →❌Incomplete
MTCNA Course Manual – IP Packet Structure:
“An IP packet always contains a source and destination IP address in the Layer 3 header. This allows routing to function across networks.”
René Meneses Guide – Packet Flow:
“IP headers are designed to carry the minimal information necessary for routing. That includes the source and destination IPs.”
Terry Combs Notes – Header Fields:
“Two IPs: one for sender, one for receiver. That’s all you’ll find in the IP header.”
Answer: BQUESTION NO: 21 [Routing]
When viewing the routes in Winbox, some routes will show "DAC" in the first column. These flags mean:
A. Dynamic, Active, Console
B. Dynamic, Active, Connected
C. Direct, Available, Connected
D. Dynamic, Available, Created
Answer: B
MikroTik’s RouterOS assigns flags to routing table entries to describe how they were created and their status.
D = Dynamic (added automatically by the system)
A = Active (currently used by RouterOS)
C = Connected (directly connected subnet or interface)
Thus, "DAC" means:
→ Dynamic, Active, Connected✅
Other flags that may appear include:
S = Static (manually added)
R = RIP
O = OSPF
B = BGP
MTCNA Course Manual – Routing Flags:
“DAC means that the route is dynamically added by the system, is currently active, and is directly connected to the device.”
René Meneses MTCNA Guide – Routing Table Interpretation:
“Flags help identify how the route was installed and its type. DAC is common for directly connected interfaces.”
Terry Combs Notes – Route Flags Table:
“DAC = Dynamic + Active + Connected. Usually appears after setting IP address on interface.”
Answer: BQUESTION NO: 22 [RouterBOARD Hardware]
In which situations Netinstall can not be used to install RouterOS on a RouterBOARD?
A. The router is connected only to a secondary Ethernet port
B. The router does not have an operating system
C. The router is connected only to a wireless network
D. The password of the router is not known
Answer: C
Netinstall is a MikroTik utility used to reinstall or upgrade RouterOS. It requires a direct Ethernet connection to the router’s first Ethernet port and works via PXE (boot over Ethernet). It cannot function over wireless.
Let's review the options:
A. The router is connected only to a secondary Ethernet port →❌Netinstall works if booted over that port
B. The router does not have an operating system →❌This is the purpose of Netinstall
C. The router is connected only to a wireless network →✅Correct: Netinstall requires a wired Ethernet connection
D. The password of the router is not known →❌Netinstall bypasses current OS; password irrelevant
MTCNA Course Manual – RouterBOARD Recovery and Netinstall:
“Netinstall must be done over a wired Ethernet connection. Wireless booting is not supported.”
René Meneses Guide – System Recovery:
“Netinstall needs Layer 2 communication via Ethernet. It cannot operate over Wi-Fi.”
Terry Combs Notes – Netinstall Limitations:
“Netinstall does not support Wi-Fi. Must connect via Ethernet to first interface, preferably.”
Answer: CQUESTION NO: 23 [DHCP]
DHCP server is configured on a router’s ether1 interface. IP address 192.168.0.100/24 is assigned to the interface. Possible IP pools, that can be used by this DHCP server, are:
A. 192.168.0.1–192.168.0.255
B. 192.169.0.1–192.169.0.254
C. 192.168.0.1–192.168.0.99, 192.168.0.101–192.168.0.254
D. 192.168.0.1–192.168.0.14
Answer: C
The router’s interface IP is 192.168.0.100/24 → which belongs to the subnet 192.168.0.0–192.168.0.255.
However, 192.168.0.100 is already assigned to the router. So, this IP must be excluded from the DHCP pool to avoid conflicts.
C offers two valid ranges excluding .100:→ 192.168.0.1–192.168.0.99→ 192.168.0.101–192.168.0.254
Let’s evaluate other options:
A. 192.168.0.1–192.168.0.255 →❌Includes broadcast (.255) and router IP (.100) → Invalid
B. 192.169.0.1–192.169.0.254 →❌Completely wrong subnet
D. 192.168.0.1–192.168.0.14 →✅Valid but unnecessarily small
MTCNA DHCP Chapter – Address Pools:
“Make sure the pool does not include the router’s IP or the network’s broadcast address. Common errors involve overlapping pools.”
René Meneses MTCNA Guide – DHCP Configuration:
“Exclude the router’s own IP from the range. Use address pools below and above the assigned IP.”
Terry Combs Notes – DHCP Pool Tips:
“Split the pool to avoid assigning the interface IP to clients. Also avoid .0 and .255.”
Firewall NAT rules process only the first packet of each connection.
True
False
MikroTik’s NAT (Network Address Translation) is part of the connection tracking mechanism. NAT rules are applied only to the first packet of a connection. Subsequent packets belonging to the same connection are automatically handled by the connection tracking module using the same translation mappings established by that first packet.
Option Analysis:
A.✔True – NAT is evaluated only on the first packet of a new connection.
B.✘False – Subsequent packets are not re-evaluated against NAT rules.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – Firewall & NAT Section:
“NAT rules apply to the first packet in a connection. After that, RouterOS uses the tracked connection entry.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – NAT & Firewall Concepts:
“Once the initial packet matches a NAT rule, connection tracking applies it to the whole session.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – NAT Implementation:
“NAT is evaluated on the first packet. Other packets in the same connection follow the established NAT mapping.”
===========
Choose all valid host address ranges for subnet 15.242.55.62/27
15.242.55.33 – 15.242.55.62
15.242.55.32 – 15.242.55.63
15.242.55.31 – 15.242.55.62
15.242.55.33 – 15.242.55.63
/27 subnet = 255.255.255.224 → block size of 32
To determine the subnet range:
Start by finding block base:15.242.55.62 falls in the 15.242.55.32/27 subnetRange: 15.242.55.32 – 15.242.55.63Network Address = 15.242.55.32Broadcast Address = 15.242.55.63Usable Host Range = 15.242.55.33 to 15.242.55.62
Evaluation:
A. 15.242.55.33 – 15.242.55.62 →✅Valid host range
B. 15.242.55.32 – 15.242.55.63 →❌Includes network and broadcast addresses
C. 15.242.55.31 – 15.242.55.62 →❌15.242.55.31 is outside this subnet
D. 15.242.55.33 – 15.242.55.63 →❌Includes broadcast address
MTCNA Course Slides – Subnetting:
“In a /27 subnet (block size 32), the first address is the network, last is broadcast. Only the IPs in between are valid host addresses.”
René Meneses Guide – Subnetting Examples:
“A /27 includes 32 addresses. For subnet 192.168.1.32/27, usable IPs are 192.168.1.33–62.”
Terry Combs Notes – Addressing Exercises:
“Subtract 2 from total IPs in subnet for host count. Don't use .0 (network) or .255 (broadcast) equivalents.”
Answer: A
RouterOS log messages are stored on disk by default
True
False
By default, RouterOS logs are stored in RAM and are lost upon reboot. They are visible usingthe /log print command or in the Winbox log window. To store logs persistently (on disk or file), you must manually configure a logging action that writes to file or remote syslog server.
A.✘True – Incorrect. Logs are not stored persistently unless explicitly configured.
B.✔False – Correct. Logs are stored in memory (RAM) by default.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – Logging System:
“By default, log entries are stored in memory. They are not saved after reboot unless file logging is configured.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Log Settings:
“Logging to disk is optional and must be configured manually. Default action is to keep logs in RAM.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – System Logging:
“RouterOS keeps logs in memory. Use log actions to save logs to disk or send to remote syslog.”
===========
Mark all the features that can be used for limiting client registrations to your access point:
access-list
wpa
WDS
registration-table
MikroTik allows you to control which clients can connect to your access point through:
WPA/WPA2 security – prevents unauthorized devices from authenticating.
Access List – filters by MAC address and signal strength.
Option breakdown:
A.✔access-list – Used to accept/reject client MACs and customize access settings.
B.✔wpa – WPA/WPA2 passphrase restricts who can join the network.
C.✘WDS – Wireless Distribution System, used for bridging, not access control.
D.✘registration-table – A monitoring tool showing currently connected clients; it doesn’t restrict connections.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – Wireless Access Control:
“Use WPA/WPA2 for secure authentication. Access List lets you accept or reject clients based on MAC or signal level.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Wireless Security & Filtering:
“You can limit client access using WPA security and Access List. Registration Table only shows connected users.”
Extract from Terry Combs Notes – Wireless Configuration:
“Access control = WPA + Access List. WDS is for bridging, and registration-table is read-only.”
There are two wireless cards (wlan1 and wlan2) which are bridged together. On wlan1 card thereis a setting "Forwarding=no". Choose the correct answer(s):
Stations on wlan2 will be able to communicate with stations on wlan2
Stations on wlan2 will be able to communicate with stations on wlan1
Stations on wlan1 will be able to communicate with stations on wlan1
To prevent communication between wlan1 and wlan2 one cannot use Bridge Filters
Stations on wlan1 will be able to communicate with stations on wlan2
Setting "forwarding=no" on a wireless interface prevents communication between connected clients on that interface and between that interface and other interfaces in the same bridge. This means:
Stations connected to wlan1 cannot talk to each other
Stations on wlan1 cannot talk to stations on wlan2 (even if bridged)
Stations on wlan2 can talk to each other normally
Evaluation:
A.✅Correct – forwarding=no does not affect wlan2
B.❌Incorrect – forwarding=no blocks this
C.✅Correct – clients on wlan1 cannot talk to each other either
D.❌Bridge filters can be used but this scenario is about forwarding settings
E.❌Blocked by forwarding=no
MTCNA Wireless Module – Wireless Forwarding Behavior:
“Forwarding=no disables client-to-client communication on the interface and across bridges.”
René Meneses Study Guide – Wireless Access Config:
“Use forwarding=no to isolate clients on the same AP. Affects bridging too.”
Terry Combs Notes – Wireless Isolation:
“Setting forwarding=no isolates all clients on that wireless card.”
Answer: A, CQUESTION NO: 81 [Wireless]
Consider a wireless access point with mode=ap-bridge. What is the maximum number of concurrent clients that can connect to it?
A. 2007
B. 2012
C. 2048
D. 1024
Answer: C
In MikroTik RouterOS, the theoretical maximum number of clients that can associate with an AP in ap-bridge mode is 2048. However, practical limits depend on hardware performance and network stability, and most real-world setups use far fewer clients.
Let’s review:
A. 2007 →❌Close, but not the actual hard limit
B. 2012 →❌Incorrect
C.✅2048 → Correct per MikroTik’s AP mode specification
D. 1024 →❌Lower than the actual maximum
MTCNA Wireless Module – AP Behavior:
“In ap-bridge mode, the maximum theoretical client limit is 2048. Actual stable operation may be lower.”
René Meneses Guide – Wireless Scaling:
“2048 is the upper limit for client associations on a MikroTik AP in bridge mode.”
Terry Combs Notes – Client Capacity:
“2048 clients = maximum. Performance may degrade before that in high-traffic environments.”
Mark all packages required for PPPoE server on MikroTik RouterOS
ppp
user-manager
radius
synchronous
system
The PPPoE server functionality in RouterOS relies primarily on the PPP package, which includes support for protocols like PPP, PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP, SSTP, etc. The system package is also always required, as it contains the core OS components.
Option breakdown:
A.✔ppp – Required. Contains all PPP and PPPoE server/client implementations.
B.✘user-manager – Optional. Used for advanced AAA (authentication/accounting), not required for basic PPPoE.
C.✘radius – Optional. Used for external authentication, not essential unless RADIUS integration is needed.
D.✘synchronous – Used for legacy synchronous interfaces (e.g., serial or modem), not for PPPoE.
E.✔system – Required for all RouterOS functions.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – RouterOS Packages:
“To enable PPPoE server functionality, you need the ppp and system packages. Radius and User Manager are optional.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – PPPoE Deployment:
“Only the ppp and system packages are strictly required. Additional features like radius are for centralized authentication.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – RouterOS Package Descriptions:
“ppp: required for PPP, PPTP, L2TP, PPPoE; system: required core package. user-manager and radius are optional.”
===========
Which command is used to upgrade an IOS on a Cisco router?
copy tftp run
copy tftp start
config net
copy tftp flash
To upgrade or install a new Cisco IOS image on a router, you typically copy the IOS image file from a TFTP server into the router’s flash memory. The correct syntax is:
copy tftp flash
This command tells the router to copy the IOS image from a TFTP server into flash storage, where it can be booted.
Cisco IOS Documentation – Image Upgrade Process:
“Use the command copy tftp flash to transfer an IOS image from a TFTP server to the router’s flash memory.”
Other options:
A: copy tftp run – invalid; you cannot copy into the running-config that way
B: copy tftp start – used to copy configuration, not IOS image
C: config net – an older and deprecated command, not for IOS upgrades
Final Answer: DQUESTION NO: 122 [RouterOS Introduction – ICMP and Diagnostics]
Which protocol does Ping use?
A. TCP
B. ARP
C. ICMP
D. BootP
Answer: C
Ping is a diagnostic utility used to test reachability between devices. It sends ICMP Echo Request packets and waits for ICMP Echo Replies. ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is used for these types of control messages and is encapsulated within IP.
MTCNA Course Material – Diagnostic Tools:
“Ping uses ICMP Echo Requests to verify if a destination is reachable. It does not use TCP or UDP.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Ping and ICMP:
“Ping uses ICMP, not TCP or ARP. ICMP packets are used to check basic connectivity.”
MikroTik Wiki – Ping Tool Description:
“Ping works by sending ICMP packets. It cannot use TCP.”
Other options:
TCP: Used by protocols like HTTP, FTP
ARP: Resolves IP to MAC, not used for ping
BootP: DHCP-related protocol, not diagnostic
Final Answer: CQUESTION NO: 123 [Cisco – Frame Relay Troubleshooting]
What command will display the line, protocol, DLCI, and LMI information of an interface?
A. sh pvc
B. show interface
C. show frame-relay pvc
D. show run
Answer: C
In Cisco IOS, to display detailed Frame Relay virtual circuit information, including the line status, protocol status, DLCI (Data Link Connection Identifier), and LMI (Local Management Interface) details, the correct command is:
show frame-relay pvc
Cisco IOS Command Reference – Frame Relay:
“The show frame-relay pvc command displays information about PVC status, including DLCI numbers and LMI statistics.”
Breakdown:
A: sh pvc – shorthand and ambiguous, may not be recognized
B: show interface – general interface stats but lacks detailed LMI/DLCI info
C: show frame-relay pvc –✔correct, provides detailed DLCI/LMI info
D: show run – shows current configuration, not real-time PVC status
Final Answer: CQUESTION NO: 124 [Networking Fundamentals – Ethernet and Switching]
How many collision domains are created when you segment a network with a 12-port switch?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 5
D. 12
Answer: D
Each port on a switch creates its own collision domain. Unlike hubs (which extend a single collision domain), switches segment each interface, allowing full-duplex communication and eliminating collisions.
MTCNA Course Material – Ethernet Switching Concepts:
“Each switch port is a separate collision domain. A 24-port switch creates 24 separate collision domains.”
René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Collision and Broadcast Domains:
“Switches break up collision domains per port, unlike hubs.”
Therefore, a 12-port switch creates 12 individual collision domains.
NAT rule is going to catch SMTP traffic and send it to a specific mail server. What is the correct action for a NAT rule?
passthrough
dst-nat
redirect
tarpit
To redirect SMTP (port 25) traffic from users to a specific internal or external SMTP server, you must use dst-nat. This modifies the destination address and port to point to the desired mail server.
A.✘passthrough – Allows the packet to be evaluated by other NAT rules; it doesn't alter traffic
B.✔dst-nat – Rewrites destination IP/port; this is what is needed to redirect SMTP to a specific server
C.✘redirect – Sends traffic to the router itself; not suitable for external redirection
D.✘tarpit – Used for slowing down malicious TCP connections, not redirection
Extract from MTCNA Course Material – NAT Types:
“Use dst-nat to change the destination IP address. This is suitable for port forwarding or service redirection.”
Extract from René Meneses Study Guide – NAT Rules:
“To redirect traffic to a specific server, use action=dst-nat and specify the new destination address.”
===========
Bridging loops can be avoided by enabling:
RSTP protocol
STP protocol
Connection tracking
UDP filter
ICMP filter
Bridging loops occur when there are multiple active paths between switches or bridge interfaces, causing broadcast storms or MAC table instability. MikroTik RouterOS supports both STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) and RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) to detect and block redundant paths.
A.✔RSTP – Faster and preferred protocol to prevent loops.
B.✔STP – The original protocol, slower convergence but still effective.
C.✘Connection tracking – Not related to Layer 2 loop prevention.
D.✘UDP filter – Filters specific traffic types, doesn’t handle loops.
E.✘ICMP filter – Not relevant to Layer 2 loop protection.
Extract from Official MTCNA Course Material – Bridging and STP:
“STP or RSTP must be enabled to prevent bridging loops. RSTP is the recommended version due to faster convergence.”
Extract from René Meneses MTCNA Study Guide – Bridging:
“Always enable STP or RSTP when using bridges with multiple paths to prevent Layer 2 loops.”
Extract from MikroTik Wiki – STP / RSTP:
“STP and RSTP are loop prevention mechanisms for bridges. They dynamically block redundant links.”
===========
Copyright © 2014-2026 Examstrust. All Rights Reserved
