You are asked to see a 30-year-old woman, gravida 8, para 4, aborta 1, for symptoms of postpartum depression. She immigrated to Canada 8 months ago. She has been reluctant to speak to members of the medical team without her family members, even when an interpreter is present. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 37-year-old man presents with chronic back, neck, and shoulder pain following a workplace injury 4 years ago. He has a history of alcohol misuse and PTSD related to the incident. Current medications (acetaminophen, naproxen, amitriptyline, gabapentin) provide inadequate pain relief. He requests oxycodone after self-trialing it with temporary benefit. After history and physical assessment, which one of the following is the best next step?
A 20-year-old nulligravid woman presents with severe pain during menstruation. She is unable to take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and is adamant about not taking any hormonal therapy. She has questions about non-medicinal therapeutic options. Which one of the following recommendations is the most appropriate?
A 68-year-old man with a history of diabetes, hypertension, delirium tremens, and tobacco addiction comes to the Emergency Department with his daughter. She tells you that his behavior has become unmanageable and she feels he may require an increased level of care. His vital signs are:
Blood pressure: 162/105 mm Hg
Heart rate: 112/min, regular
Temperature: 37.8°C
On history, his daughter explains she had to confiscate a half-empty bottle of alcohol from his room yesterday. He is now convinced that there are bugs crawling all over him and he will not relax. He appears pale, sweaty, and shaky. His most recent blood glucose is 7.8 mmol/L (3.8–11.1). Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 9-year-old girl is brought to the Emergency Department because she has generalized urticaria, abdominal cramping, and postural dizziness 30 minutes after eating at a friend’s birthday party. Which one of the following is the most appropriate route of administration for epinephrine?
A 66-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer presents with hard, difficult-to-pass stools. She has been experiencing this issue since starting morphine to control her pain. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 60-year-old man presents to the office with concerns regarding a pruritic rash, which he has had for several years. He reports a “crawling” sensation on his skin. He is concerned that this rash may be caused by a parasite he may have picked up while serving in the military overseas. On examination, you note multiple crusted lesions on his forearms, neck, chest, scalp, and thighs. There is a complete sparing of the skin on his back. He brought a bottle with fibrous material of different colours that he picked from his wounds. He is otherwise healthy and reports no other symptoms except some chronic fatigue and insomnia related to the itching. Which one of the following treatments is the most appropriate?
A 20-year-old man is brought by a friend to the emergency department with an elevated temperature, generalized muscle rigidity, hypovolemia, a fluctuating level of consciousness, and impaired attention. The patient also may be responding to auditory hallucinations. The friend informs you that the patient overdosed with a prescribed medication. Which one of the following medications is most likely to cause these symptoms?
A 4-year-old girl is brought to the family practice by her father. The child has a 2-week history of low-grade fever, fatigue, and sore throat. She has also developed several small, round, mildly tender lumps bilaterally in her neck. She was previously well. Which one of the following is most likely to be found on abdominal examination?
An 80-year-old woman presents to your office with weight loss and generalized weakness. Her husband calls you after the appointment and asks that his wife not be told if she is diagnosed with cancer as hearing this will likely "kill her." Investigations subsequently show that she has metastatic lung cancer. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 38-year-old man is brought by his wife to the Emergency Department with fatigue, dizziness, and nausea after completing a hiking tour on a hot, humid day. His wife became worried after he had collapsed. He has been sweating heavily and vomited twice on the drive in. His medical history is unremarkable, and he takes no medications. His vital signs on arrival are as follows:
Blood pressure
85/57 mm Hg
Heart rate
120/min
Respiratory rate
18/min
Temperature
40.1 °C
Oxygen saturation
95%, room air
—
On physical examination, the patient's skin is dry, flushed, and warm to the touch. He has a diffuse erythematous papular rash. Findings of a thorough physical examination are otherwise unremarkable. An electrocardiogram shows sinus tachycardia. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 70-year-old man presents with severe, postprandial, mid-abdominal pain which has become more severe over the past 6 to 9 months. It is associated with nausea but has not caused him to vomit or changed his bowel habits. He has lost 14 kg over the last 6 months. Abdominal and rectal examination is normal. Upper gastrointestinal series is unremarkable. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 40-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of severe abdominal pain and recurrent vomiting. He has a long-term history of alcohol use disorder. His blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and his heart rate is 120/min. The pain is located mostly in the epigastrium but radiates to the right upper quadrant and to his back. Radiographs of the abdomen and chest reveal some distended small bowel loops in his upper abdomen. Laboratory work results are pending. After fluid resuscitation, which one of the following is the best next step?
A 6-week-old boy is brought to your office by his parents for a follow-up following a recent urinary tract infection. His abdominal ultrasound shows dilated urinary bladder and ureters as well as bilateral hydronephrosis. Which one of the following historical findings would be most helpful in establishing the correct diagnosis?
A 25-year-old woman who is at 8 weeks' gestation plans to travel to rural Cambodia to care for her ill mother. Which one of the following treatments should be provided to her before the trip?
A 30-year-old woman presents to your office with a 6-week history of left lower quadrant pain and dyspareunia. A pelvic ultrasound is normal. Which one of the following is the most important immediate investigation?
A 76-year-old man is brought by his family to your clinic with new-onset urinary incontinence. They state that the patient is experiencing a slowly progressing cognitive decline marked by memory disturbance, apathy, and attentional problems. Examination reveals that the patient has a stooped, forward-leaning posture and a wide-based gait. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 15-year-old boy is brought to the office by his father because he is having headaches. When alone, the boy appears withdrawn and admits to suicidal ideation. He shares that he is gay but does not want to tell his parents. He says that he faked the headaches so that one of his parents would make an appointment for him. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 21-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with a 6-month history of unusual behavior. He believes that he has been specially chosen to found a new religion. He says he has seen visions of angels in his bedroom. He appears disheveled and malodorous. On further inspection, you note that he drinks 2 liters daily. Which one of the following is the most appropriate initial management?
A 38-year-old marathon runner presents to your office with a 6-month history of increasing right hip pain. The pain is worse with acclivity and has prevented him from running for the last 4 months. He denies fever or chills. His wife adds that she is concerned because he is increasingly disengaged with the family and not interested in other activities he usually enjoys, including sex. Which one of the following is the best next step in management?
A 29-year-old man comes to the office for an initial visit. He is being treated for schizophrenia and epilepsy. He has a 20 pack-year history of smoking. His medications are carbamazepine, clozapine, and quetiapine. In the past year, he has gained a considerable amount of weight. Asidefrom a BMI of 32, the results of his physical examination are unremarkable. Which one of the following conditions should he be investigated for?
Your colleague's receptionist asks you to assess her 4-year-old daughter who has had 2 episodesof acute otitis media in the last month. The mother wants you to arrange a consultation with an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist to get a tympanostomy before her daughter starts school. You do not believe there is a surgical indication at this time. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 42-year-old man presents to your office with acute left knee pain and difficulty walking. He denies any trauma. He reports 2 painful episodes involving his right great toe in the last year. He smokes half a pack of cigarettes a day and drinks at least 3 beers daily. He has a temperature of 38.2°C and has a red, swollen and warm left knee. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 30-year-old man (assigned female at birth) presents to your clinic for a periodic health examination. He declines a gynecologic examination because such examinations lead to intense emotional distress for him. He also believes that he does not require a Papanicolaou (Pap) test because he is not in a sexual relationship with a man. After acknowledging the patient's distress and providing education regarding the need for Pap screening, which one of the following would be the best next step?
A 2-year-old boy is brought by his parents to your clinic because of sudden onset of high fever, refusal to drink, and drooling. Examination reveals cervical lymphadenopathy as well as multiple ulcers on the inner lips, tongue, and gums. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 65-year-old woman presents to the office for follow-up regarding vaginal bleeding. Her last visit was 2 months ago. At that visit, the results of a pelvic examination and a Papanicolaou test were normal. She also had an endometrial biopsy but there was "insufficient material for diagnosis." She reports that she is still losing small amounts of blood almost every day. On history, she has been taking continuous combined hormone replacement therapy for 10 years because of vasomotor symptoms. Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
You have been asked to develop a program in your hospital for people who are at the highest risk of death by suicide. The hospital administrator asks you to describe the types of patients they should expect in the program. Which one of the following groups is the most likely prominent demographic?
A 45-year-old man with a developmental delay and a history of disruptive behavior presents to the clinic looking for his family doctor. He is well known to the clinic. He appears drunk and has accidentally broken 2 large beer bottles in the waiting room but remains calm. The office staff requests your help to deal with this situation. Which one of the following is the most appropriate initial step?
A 59-year-old woman comes to the office because her 48-year-old sister was recently diagnosed with cervical cancer. Your patient thinks her mother may have also had cervical cancer. A Papanicolaou (Pap) test performed 16 months ago had normal results, as did all previous Pap tests. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 24-year-old woman presents with rapidly increasing lower leg pain. Less than 24 hours ago, she fell off her bicycle and had some minor abrasions. On examination, she is in severe pain and appears anxious. Local examination of her leg reveals mild discoloration with marked tenderness but no swelling in her calf. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 17-year-old boy presents to your clinic with a 6-month history of recurrent headaches. The headaches are excruciating, and he describes them as a stabbing pain, usually around his right eye. They occur several times daily for 2 to 3 weeks and recur every few months. The headaches are associated with tearing from his right eye and tend to get worse when he is overtired. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
An intoxicated 28-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Department after being found in the snow. His vital signs are as follows:
Temperature: 33°C
Respiratory rate: 22/min
Heart rate: 123/min
The patient is shivering and displays some dysarthria and ataxia. After his wet clothing is removed, he is provided with a warm blanket. The results of the subsequent physical examination are unremarkable, except for frostbite of the ears and fingers. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 60-year-old man has a strong family history of aortic aneurysms. Screening abdominal ultrasonography reveals an incidental <1 cm mass in his left kidney. Computed tomography confirms that the mass is consistent with renal adenocarcinoma. Which one of the following is the most appropriate step in management?
You are evaluating a 75-year-old man with recently diagnosed prostate cancer and 2 painful metastases of the lumbar spine. Which one of the following therapeutic options is the most appropriate?
A 55-year-old man presents with vague abdominal pain and general weakness. His mother had colon cancer and died at age 60 years. His physical examination findings and complete blood count results are normal. Which one of the following tests should be ordered first?
A 25-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with diffuse abdominal pain and anorexia. He was tackled in a football game yesterday. He reports a 3-week history of sore throat and fatigue. Vital signs are as follows:
Blood pressure: 95/45 mm Hg
Heart rate: 96/min
Temperature: 37.6°C
Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 39-year-old man presents to a psychiatrist. He says, "It often seems to me that I am not part of this world. My voice sounds strange to me, and other people seem like figures in a dream." He has had these feelings intermittently for about 2 years. There is no history of hallucinations, and there are no current indications of disorganized thinking. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 70-year-old hypertensive woman with a history of congestive heart failure (CHF) secondary to left ventricular dysfunction presents to your office with a persistent dry hacking cough. She claims it began when she was started on ramipril. Which one of the following medications would be most appropriate to replace ramipril, to ensure that the risk of morbidity associated with CHF remains low?
A 58-year-old woman presents to your office with heavy vaginal bleeding. She has a history of type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Some active bleeding is visible on speculum examination. Ultrasound reveals an endometrial thickness of 12 mm. Endometrial biopsy shows complex hyperplasia with atypia. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 55-year-old woman presents to the office with a 2-month history of right shoulder pain and limited function that started after she began an upper body weight training program. Examination shows tenderness inferior to the acromion. She has full passive range of motion of the shoulder but significant pain with abduction from 30° to 120° of arc. Which one of the following is the best next step?
Which one of the following bodies decides whether a physician is permitted to practise medicine in a province or territory?
A 27-year-old woman presents with an enlarged thyroid. She had not noticed it herself until her mother brought it to her attention. She is asymptomatic from an endocrine perspective, and her serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is normal.
Which one of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A 71-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Department with sudden onset of shortness of breath and chest pain. He was discharged from hospital 1 week ago after a total hip arthroplasty. On examination, his respiratory rate is 32/min. There is visible respiratory distress, and chest auscultation is clear. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 29-year-old woman presents with vaginal spotting after 6 weeks of amenorrhea. She is asymptomatic otherwise. Serum β-hCG is 2150 IU/L, and pelvic ultrasound shows an empty uterus. She has been trying to conceive for 7 months. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 35-year-old man comes to your office with a history of headaches that last 1 hour and are relieved by 1000 mg of acetaminophen. These headaches, which started 6 months ago after he got his first job as a lawyer, occur regularly. The patient wants a computed tomography scan of his head to rule out a tumour. Physical examination reveals no abnormality. Review of systems does not contribute any positive findings. Which one of the following is the best management?
A 32-year-old primigravid woman is receiving magnesium sulfate for tocolysis. Her pregnancy is at 26 weeks' gestation. You suspect magnesium sulfate toxicity. Which one of the following is the first sign of magnesium sulfate toxicity?
A 21-year-old man presents to the office with persistent pain and swelling of the wrist 2 weeks after falling on his outstretched hand. Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the wrist taken at the time of the injury showed no evidence of fracture or dislocation. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of the patient's symptoms?
A 55-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of poor memory and impaired concentration. She has bipolar I disorder that has been treated with lithium carbonate for 4 years. She has gained a lot of weight since starting lithium. Physical examination findings are otherwise normal. She is concerned about her memory issues, but there are no other perception, mood, or cognition abnormalities. Which one of the following tests is most likely to have abnormal findings?
You are caring for a 17-year-old girl who has end-stage renal disease. She is receiving dialysis at the hospital 3 times a week. She requests medical assistance in dying (MAID). Which of the following is the best next step?
A young man and woman who are in a relationship present to the office for prenatal counselling. During the visit, you observe that the man's lips appear as shown in the referenced photo.
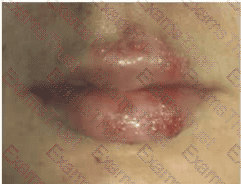
[Image shows grouped vesicular lesions on erythematous base affecting the lips—classic for herpes labialis (HSV-1).]
Which one of the following is the best advice?
A 14-year-old girl is brought to the Emergency Department with a 20-minute history of difficulty breathing that started during a school assembly. She has had similar symptoms 3 times in the last 2 weeks. These episodes develop rapidly and resolve gradually over several minutes. She reports tingling in her fingers and toes. On examination, her vital signs are as follows:
Blood pressure
120/80 mm Hg
Heart rate
100/min
Respiratory rate
22/min
Oxygen saturation on room air
95%
Temperature
36.9 °C, orally
Apart from mildly dilated pupils, her examination is otherwise normal. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
There are many expenses which are considered part of providing care to patients. Under Canadian legislation, which one of the following is an acceptable means of covering these costs?
The parents of a 12-year-old boy present to your clinic to discuss their son’s submersion injury. The patient was seen in hospital for 6 months after being pulled unresponsive from a lake at his friend’s house; he had been submerged for an estimated 20 minutes. After extended resuscitation and a 2-month stay in the intensive care unit, he remains in a persistent vegetative state but needs no respiratory or cardiac support. When evaluating the discharge from hospital, which one of the following is most appropriate?
A 9-year-old girl from a remote community is brought to the clinic with a 2-week history of swelling in her neck. She has been afebrile but has had some night sweats. On examination, you note a fixed, unilateral, and nontender supraclavicular lymph node measuring 3 cm. The overlying skin color is unremarkable. In addition, you note a slightly enlarged spleen and liver. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 53-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with a 3-week history of believing his neighbor is poisoning him by pumping gas through his home’s air vent. He appears distracted, irritable, and is speaking very quickly. He has a family history of depression. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A 30-year-old woman presents to the office with her partner and reports that they are planning for her to conceive soon. They visited Mexico recently and are concerned about exposure to the Zika virus. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, presents for her 1st antenatal visit. She states she is at 26 weeks' gestation and is healthy. On abdominal examination, her fundus is palpated at the umbilicus. Which one of the following is the most likely explanation for this finding?
A 48-year-old woman presents with a 2-year history of regular, heavy menstrual flow. She has a BMI of 54, poorly controlled type 2 diabetes, and obstructive sleep apnea. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin: 82 g/L (123–157)
Ferritin: 6 µg/L (11–307)
Endometrial biopsy: Absence of hyperplasia or malignancy
Transvaginal ultrasound:
• Uterus: 12 cm × 8.2 cm × 6 cm
• Intramural fibroids
• Endometrial thickness: 14 mm
• Ovaries: Normal
Which one of the following is the best next step?
A same-sex couple asks to join a family physician’s practice. The physician tells them that shedoes not treat same-sex couples and will refer them to a physician with more clinical experience with same-sex couples. Which one of the following best describes the physician’s obligation under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms?
A 62-year-old woman is referred to your clinic for evaluation of hypercalcemia. She has a history of hypertension and vitamin D deficiency. Her medications include hydrochlorothiazide and vitamin D supplements. Laboratory investigations are as follows:
Calcium: 2.72 mmol/L (↑)
Phosphate: 0.9 mmol/L (↓)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH): 0.9 pmol/L (↓)
25-hydroxy vitamin D: 80 nmol/L (normal)
Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 39-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, aborta 0, presents with concerns that a friend has recently suffered from postpartum psychosis. She wonders if she is likely to suffer this disorder following delivery of her 2nd child. Which one of the following is most likely to increase your patient's risk?
A 23-year-old woman with borderline personality disorder is brought to the Emergency Department having ingested non-lethal substances after her boyfriend broke up with her. The staff tells you that she has consulted 8 times under similar circumstances in the past 3 years. Which one of the following pieces of information would be useful to provide to the staff?
A 22-year-old woman presents to the office for episodic mood changes that her boyfriend has noticed. During such episodes, she cries suddenly, is irritable and sad, and withdraws from socializing. Which one of the following would be most useful in establishing a diagnosis?
One of your patients presents to your clinic for a consultation regarding their recurrent hemoptysis. On review of their chart, you realize that although you had ordered chest radiography 2 months ago, the result cannot be found in the chart. You call the radiology department and are relieved to find that the chest radiography was done and that it did not reveal any pathology. After informing the patient of this lapse in reporting, which one of the following is the best next step?
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, presents with a positive pregnancy test. Her previous pregnancy was associated with preeclampsia, and she delivered a 1000 g boy at 34 weeks' gestation. Her blood pressure is 130/86 mm Hg. Which one of the following is the best recommendation for this pregnancy?
A 69-year-old woman with long-standing hypertension presents to the emergency department with a 2-hour history of persistent chest and back pain. A posteroanterior chest radiograph shows suspicious widening of the mediastinal shadow. Which one of the following is most likely to yield a clinical diagnosis?
A surgical clinic would like to respond to the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada: Calls to Action report. The clinic has implemented a mandatory cultural safety course for all employees and ongoing faculty development that includes teachings from Elders and Knowledge Keepers and teaching sessions about harm reduction, trauma-informed care, and antiracism. Which one of the following steps would further the clinic's goal of responding to this report?
A 15-year-old boy is brought to your office because of concerns about his breast development. He has no other symptoms. His physical examination does not reveal any other abnormality. Which one of the following is the best next step?
A 10-year-old girl is brought to the Emergency Department by her mother because her daughter is crying and says she "can’t pee." Her daughter fell on the monkey bars at school earlier that day. On examination, there is a large vulvar bruise anteriorly. Which one of the following is the best next step?