Desktop users on the same FusionAccess can be authenticated using different domains.
TRUE
FALSE
As detailed in the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training material regarding FusionAccess Service Provisioning, the statement is TRUE. Huawei FusionAccess is designed to support complex enterprise environments, including multi-domain architectures. This is particularly relevant for large corporations that have acquired other companies or have organized their IT infrastructure into a forest of multiple Active Directory (AD) domains.
FusionAccess achieves this by establishingTrust Relationshipsbetween the "Management Domain" (where the infrastructure components like HDC and ITA are located) and the "User Domains" (where the desktop users' accounts are stored). When trust is correctly configured between AD domains, theHDC (Huawei Desktop Controller)can query and authenticate users across these boundaries. For instance, a user from marketing.huawei.com and another from research.huawei.com can both log into the same Web Interface (WI) and access their respective virtual desktops.
During the service provisioning process, the administrator adds the various domains to the FusionAccess management system. When a user logs in, they specify their domain prefix (e.g., DOMAIN_A\username), and the system routes the authentication request to the appropriate Domain Controller. This multi-domain support is critical forMulti-tenancyand large-scale enterprise consolidation. It allows a single, unified FusionAccess platform to serve multiple organizational units without requiring all users to be migrated into a single, massive AD domain. This logical separation is a key feature taught in the HCIA curriculum to demonstrate the scalability and flexibility of Huawei's virtual desktop solution.
====================
FusionAccess application policies allow users to use VM desktops. Match the following application scenarios with their operations
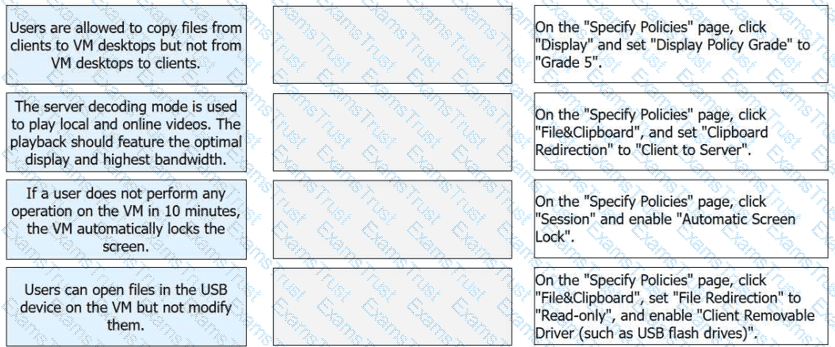
1-B, 2-A, 3-C, 4-D
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing documentation, FusionAccess application policies are critical for tailoring the virtual desktop experience to specific security and performance requirements. The Huawei Desktop Protocol (HDP) management interface allows administrators to configure granular controls over data flow, display quality, and session behavior.
For Scenario 1, setting Clipboard Redirection to "Client to Server" ensures a one-way data flow. This allows users to copy text or files from their local physical client into the virtual machine (VM) while preventing the extraction of data from the VM back to the local device, thus protecting sensitive corporate information. In Scenario 2, the Display Policy Grade determines the balance between visual fidelity and network consumption. Grade 5 is the highest setting, designed for high-performance networks (25 Mbit/s or higher), and is optimized for server-side video decoding to provide the best possible playback quality.
Scenario 3 addresses security during periods of inactivity. By enabling the "Automatic Screen Lock" under the Session policy, the system monitors user input and automatically secures the desktop if no activity is detected within the specified interval (such as 10 minutes), preventing unauthorized access to an unattended terminal. Finally, Scenario 4 utilizes File Redirection to control external hardware access. By setting this policy to "Read-only" and enabling "Client Removable Driver," users can view and open files stored on their local USB flash drives within the VM environment but are strictly prohibited from saving or modifying any data back onto those physical devices. These configurations demonstrate the robustness of Huawei’s VDI policy engine in balancing user productivity with stringent security protocols.
Match the following VLAN interface types with their descriptions.
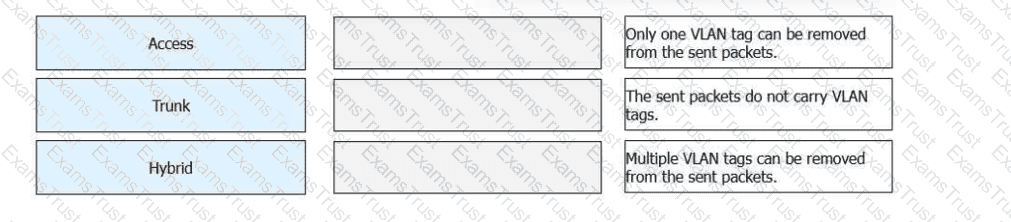
Access Interface
➡The sent packets do not carry VLAN tags.
An access interface belongs to only one VLAN.
Frames are sent untagged, making it suitable for end devices such as PCs and printers.
Trunk Interface
➡Only one VLAN tag can be removed from the sent packets.
A trunk interface allows multiple VLANs to pass.
Typically used for switch-to-switch connections.
Only the native VLAN is sent untagged; other VLANs are tagged.
Hybrid Interface
➡Multiple VLAN tags can be removed from the sent packets.
A hybrid interface supports both tagged and untagged VLAN traffic.
Multiple VLANs can be configured to send traffic without VLAN tags.
Commonly used for server connections and virtualization environments.
A router manages path information by managing its___
Routing Table
As defined in the "Network Technology Basics" module of the HCIA-Cloud Computing training, a router is a Layer 3 (Network Layer) device responsible for interconnecting different network segments and selecting the optimal path for data packets. To perform this function, the router maintains and manages a Routing Table. This table is the "map" of the network that the router uses to make forwarding decisions. Every entry in the routing table typically includes several key parameters: the destination network address, the subnet mask, the protocol (how the route was learned, such as Static, OSPF, or BGP), the preference value, the cost (metric), and the next-hop address or outbound interface.
When a router receives an IP packet, it examines the destination IP address and performs a lookup in its routing table to find the most specific match (longest match rule). If a matching entry is found, the router encapsulates the packet into a new frame and sends it toward the next hop. If no match is found and no default route exists, the packet is discarded. This process is fundamental to the operation of a Cloud Data Center where multiple Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and subnets must communicate through virtual or physical routers.
While a switch manages a MAC address table to forward frames at Layer 2, and a host manages an ARP table to map IP addresses to MAC addresses, only the routing table provides the cross-network path intelligence required for routing. In Huawei’s virtualization solutions, virtual routers within the software-defined networking (SDN) layer use these same logic principles to ensure that traffic between virtual machines in different subnets is directed efficiently to the correct destination. Proper management of the routing table is therefore the cornerstone of network reachability in cloud environments.
====================
In compute virtualization, which of the following is the operating system running on a virtual machine (VM)?
Hypervisor
Host OS
Guest OS
Host machine
The HCIA–Cloud Computing syllabus defines clear terminology for virtualization components.
The Guest OS is the operating system installed and running inside a virtual machine. It operates as if it were running on physical hardware, but all hardware access is abstracted by the hypervisor.
The hypervisor (A) is the virtualization layer that manages physical resources and virtual machines.
The host OS (B) is the operating system running on the physical server (in hosted virtualization models).
The host machine (D) refers to the physical server itself.
Therefore, the correct answer is Guest OS.
Which of the following statements are true about the differences between OpenStack and FusionCompute?
OpenStack is open-source software, and FusionCompute is closed-source commercial software.3
OpenStack does not have any virtualization capability, while FusionCompute can directly pool physical hardware resources.
OpenStack can manage VMs, bare metal servers, and containers, but FusionCompute cannot manage containers.
OpenStack has concepts about projects and tenants, but FusionCompute does not have the concept about tenants.
As covered in the "Cloud Computing Trends" and "Huawei Cloud Solutions" modules of the HCIA curriculum, OpenStack and FusionCompute occupy different layers of the cloud stack. Statement A is correct: OpenStack is a global open-source project maintained by a community, whereas FusionCompute is Huawei’s proprietary commercial virtualization platform (hypervisor).4
Statement B captures a fundamental technical difference. OpenStack is anorchestratoror "Cloud OS"; it lacks an internal hypervisor and must rely on external technologies (like KVM, Xen, or FusionCompute itself) to perform the actual virtualization. In contrast, FusionCompute is a standalonevirtualization suitethat includes the CNA (hypervisor) and VRM (management), allowing it to directly pool and manage physical hardware resources.
Statement C highlights the broader scope of OpenStack, which is designed to manage heterogeneous resources, including Bare Metal (Ironic) and Containers (Zun/Magnum). FusionCompute is a specialized tool primarily focused on Virtual Machines (VMs). Finally, Statement D refers to theMulti-tenancymodel. OpenStack was built for public and large private clouds, using "Projects" and "Tenants" to strictly isolate resources and billing between different organizations. FusionCompute is a lower-level resource manager that focuses on "Clusters" and "Resource Pools" rather than the complex tenant-based isolation logic found in high-level cloud platforms. In the Huawei ecosystem, FusionCompute often serves as the "Computing" component underneath a largerHuawei Cloud Stackor OpenStack-based solution, illustrating how these two technologies complement each other in a modern data center.
In Huawei FusionCompute, which of the following functions enables virtual machines (VMs) to be migrated between CNA hosts with different CPU models?
Cluster I/O ring adaptation
Cluster HANA optimization
Cluster Guest NUMA policy
Cluster IMC policy
In FusionCompute, VM live migration between hosts withdifferent CPU modelsrequires CPU instruction compatibility. Huawei provides theIMC (Instruction Masking Compatibility) policyat the cluster level to address this issue.
TheCluster IMC policymasks advanced CPU instruction sets so that VMs only see a common subset of CPU features supported by all hosts in the cluster. This ensures that a VM can migrate safely between CNA hosts with different CPU generations or models without encountering instruction incompatibility errors.
Other options are unrelated:
I/O ring adaptationfocuses on I/O optimization.
HANA optimizationis specific to SAP HANA workloads.
Guest NUMA policyoptimizes memory access, not CPU compatibility.
Therefore, the correct answer isCluster IMC policy.
Which of the following statements isfalseabout host requirements during FusionCompute installation?
The location where the host OS is booted first must be the location where the host OS is installed.
The disk requirements of the host where the VRM is located are the same as those of other compute nodes.
If CPU virtualization is not enabled for a host, virtual machines cannot be created on the host.
FusionCompute can be installed even if there is only one host network port.
FusionCompute installation has clear host hardware and configuration requirements defined in the HCIA syllabus.
OptionAis true. The boot device must match the installation location of the host operating system to ensure system stability.
OptionCis true.CPU virtualization must be enabledin the BIOS (Intel VT-x or AMD-V). If not enabled, the host cannot run virtual machines, which is a mandatory prerequisite.
OptionDis true. FusionComputecan be installed with a single network interface, although this is not recommended for production environments. Multiple NICs are preferred for traffic separation and high availability.
OptionBis false. The host where theVRM is deployed has higher disk requirementsthan ordinary compute nodes because it runs management services, databases, and logs. Therefore, its disk requirements arenot the sameas other compute nodes.
Thus, the false statement isB.
During the deployment of the FusionAccess gateway and load balancer, the HA status is abnormal after vAG/vLB configuration. Which of the following is not a possible cause of this fault?
The administrator changed the "root" password for vAG/vLB.
The administrator changed the "root" password for HDC.
The administrator changed the "gandalf" password for vAG/vLB.
The administrator changed the password for logging in to the ITA portal.
In the official Huawei FusionAccess maintenance and troubleshooting documentation, High Availability (HA) between the vAG (Virtual Access Gateway) and vLB (Virtual Load Balancer) is maintained through backend synchronization and heartbeat checks. The correct answer is D because changing the ITA portal login password has no technical impact on the background communication between infrastructure VMs. The ITA portal password is the credential used by an administrator to log into the web management interface it is an application-layer credential stored in the database, not a system-level credential used for inter-component service discovery or HA heartbeats.
In contrast, options A, B, and C can indeed lead to "HA status abnormal." In the Huawei ecosystem, components often communicate using internal system accounts. Specifically, thegandalfaccount is the default account used for the FusionAccess management plane to log in to and manage these components. If an administrator manually changes the gandalf password on the vAG/vLB VM (Option C) without updating the corresponding credentials in the management system, the ITA will lose its ability to query the status of those nodes, resulting in an abnormal HA state.
Furthermore, while the root password (Options A and B) is generally for administrative access, the FusionAccess components are tightly integrated. Changing system-level passwords without using the official Huawei password management tools or updating the service configurations can break the scripts responsible for status reporting and synchronization. Therefore, for the HCIA exam, it is critical to understand that theITA Portal passwordis purely for the user interface and does not affect the technical "plumbing" or HA heartbeats of the underlying virtual appliances.
====================
Which of the following statements is false about CPU virtualization?
CPU virtualization includes full virtualization, paravirtualization, and hardware-assisted virtualization.
Full virtualization does not modify the guest OS. Virtual machines are highly portable and compatible and support a wide range of operating systems.
The host OS in paravirtualization supports only open-source operating systems.
Hardware-assisted virtualization does not require the CPUs to support it.
CPU virtualization is a fundamental concept in HCIA–Cloud Computing and includes multiple implementation methods.
Option A is correct. CPU virtualization is commonly categorized into full virtualization, paravirtualization, and hardware-assisted virtualization.
Option B is correct. Full virtualization allows guest operating systems to run without modification, which ensures high compatibility and portability across different platforms.
Option C is correct in the HCIA context. Paravirtualization requires modifications to the guest OS kernel, which historically limited support primarily to open-source operating systems.
Option D is false. Hardware-assisted virtualization explicitly requires CPU support, such as Intel VT-x or AMD-V. Without these features, hardware-assisted virtualization cannot function.
Therefore, the false statement is D.
Programs and data must be loaded into memory for CPU processing, and then be placed on external storage for long-term preservation.
TRUE
FALSE
The statement describes the fundamental operation of the Von Neumann architecture, which serves as the core foundation for modern server hardware used in cloud computing environments. In the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, specifically under the "Server Basics" module, the distinction between volatile and non-volatile storage is emphasized as a critical hardware concept. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) acts as the primary compute engine but cannot execute instructions directly from secondary storage devices, such as Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) or Solid State Drives (SSDs), due to the massive latency gap between CPU clock speeds and disk access times.
Therefore, for any task to be performed, the relevant programs and data must first be loaded into the system memory, or Random Access Memory (RAM). RAM provides the high-speed, low-latency access required for the CPU to fetch and execute instructions efficiently. However, RAM is volatile, meaning all stored data is lost when the power supply is interrupted. To ensure long-term preservation and data persistence, processed results or saved files must be written back to external or secondary storage. These storage devices are non-volatile and provide the capacity needed to store operating systems, applications, and user data across reboots. In a cloud environment, such as one utilizing Huawei FusionServer Pro, this cycle of data movement between storage and memory is critical for maintaining system performance. The memory acts as a high-speed buffer for active tasks, while the storage provides the persistent layer. Understanding this hardware interaction is vital for cloud administrators because virtualization performance often hinges on the balance between memory capacity and storage I/O throughput.
====================
When a user VM uses a USB device, FusionAccess defaults to "USB Port Redirection". If the device is still unavailable, the"Device Redirection"policy can be configured.
Device RedirectionAccording to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training materials, the Huawei Desktop Protocol (HDP) offers two primary methods for handling USB peripherals: USB Port Redirection and USB Device Redirection (often referred to more broadly as high-level "Device Redirection").By default, FusionAccess utilizesUSB Port Redirection. This technology works at the physical layer, capturing the USB Request Blocks (URBs) from the client terminal and transmitting them to the virtual machine. This allows the Guest OS to "see" the raw USB device and use its own local drivers. This is the most compatible method for a wide range of devices such as specialized scanners or unique USB dongles.However, if a device is still unavailable or suffers from performance issues (common on high-latency WAN links), the administrator can configure the"Device Redirection"policy. This method operates at a higher logical level. Instead of redirecting the raw USB signals, it redirects the specific function of the device. For example, a USB flash drive can be redirected using "Client Drive Redirection," or a USB printer can be redirected via "Printer Redirection." This high-level redirection is more efficient as it optimizes the data flow for that specific device class, often providing a smoother user experience in constrained network environments. In the FusionAccess management portal (ITA), these policies are managed under "HDP Policy Management," where administrators can fine-tune which redirection method takes priority based on the specific hardware being used by the end-users.====================
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the computer's computing and control core. Mainly composed of an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and a controller, it reads and executes data according to instructions.
TRUE
FALSE
According to the HCIA–Cloud Computing curriculum underServer Basics, the CPU is defined as thecore component responsible for computation and controlwithin a computer system. The CPU executes program instructions and coordinates the operation of all other hardware components.
The CPU is primarily composed of two main functional units:
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):Responsible for performing arithmetic operations (such as addition and subtraction) and logical operations (such as comparisons and logical AND/OR).
Control Unit (Controller):Responsible for fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, and controlling the execution process by issuing control signals to other components.
The CPU operates based on thefetch–decode–execute cycle, which is a fundamental concept emphasized in HCIA learning materials. During this process, the CPU reads instructions and related data from memory, processes them, and produces results according to the instruction set architecture.
Because the statement accurately describes therole, composition, and working principleof the CPU as defined in Huawei’s HCIA–Cloud Computing documentation, it iscorrect.
Which of the following are functions of FusionCompute?
Datastores support file system formats VIMS, NFS, and EXT4.
Users can expand or reduce the memory capacity for online or offline VMs as needed.
Storage live migration is to migrate data within a storage device or between different storage devices.
VM live migration only allows VMs to migrate among hosts that share the same storage.
As detailed in the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing technical documentation, FusionCompute offers a robust suite of resource management functions. Statement A is correct: FusionCompute datastores support multiple file system formats to accommodate different storage backends. VIMS (Virtual Image Management System) is Huawei’s high-performance cluster file system used for SAN storage; NFS is used for Network Attached Storage; and EXT4 is used for local disk virtualization on a single host. This variety allows administrators to build heterogeneous storage pools.
Statement B is also a verified function. FusionCompute supports dynamic resource adjustment. Users can modify memory capacity for both offline VMs (while the VM is stopped) and online VMs (while running). Online memory expansion requires the "Hot Add" feature and Guest OS support, while reduction typically requires the VM to be in a state where the kernel can release the address space. Statement C accurately describes Storage Live Migration. This feature allows a VM's virtual disk files to be moved from one datastore to another (or within the same storage device) while the VM remains running, which is essential for storage maintenance and load balancing.
Statement D is incorrect because of the word "only." While traditional VM live migration (vMotion style) does require shared storage so that both hosts can see the same disk, modern versions of FusionCompute also support Shared-Nothing Live Migration. This technology migrates both the VM's memory state and its disk data simultaneously over the network, allowing a VM to move between hosts that do *not* share a common backend storage. Because D ignores this advanced capability, it is excluded from the list of correct functions in the context of FusionCompute's full feature set.
Which of the following statements isfalseabout virtualization concepts?
A guest OS is the operating system running on a virtual machine (VM).
A guest machine is a virtual machine (VM).
A host machine is a physical machine.
A host OS is the virtualization software layer.
The HCIA–Cloud Computing syllabus clearly defines the basic terminology used in virtualization.
OptionAis correct. Aguest OSrefers to the operating system installed and running inside a virtual machine.
OptionBis correct. Aguest machineis another term for a virtual machine (VM).
OptionCis correct. Ahost machinetypically refers to thephysical serverthat provides hardware resources for virtualization.
OptionDis false. Ahost OS is not the virtualization software layer. The virtualization layer is thehypervisor(such as KVM, Xen, or FusionCompute). In some architectures, the host OS and hypervisor may coexist, but they arenot the same concept.
Therefore, the false statement isD.
Which of the following statements about the differences between adomainand anorganizational unit (OU)aretrue?
Both OUs and domains can contain Active Directory (AD) objects.
Users can log in to a domain but not to an OU.
Group policies can be configured for both OUs and domains.
An OU can exist in a domain, and a domain can also exist in an OU.
In Active Directory (AD),domainsandorganizational units (OUs)serve different purposes.
Ais true. Both domains and OUs can contain AD objects such as users, computers, and groups.
Bis true. Authentication is performed at thedomain level. Users log in to a domain, not to an OU.
Cis true.Group Policy Objects (GPOs)can be applied at both the domain level and the OU level.
Dis false. An OU can existinside a domain, but adomain cannot exist inside an OU. Domains are top-level logical boundaries.
Therefore, the correct answers areA, B, and C.
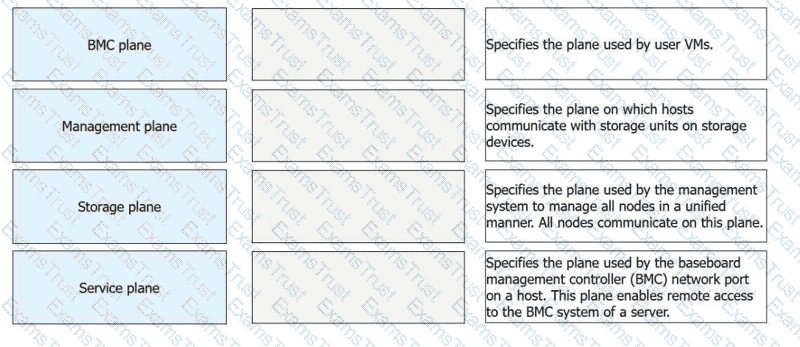
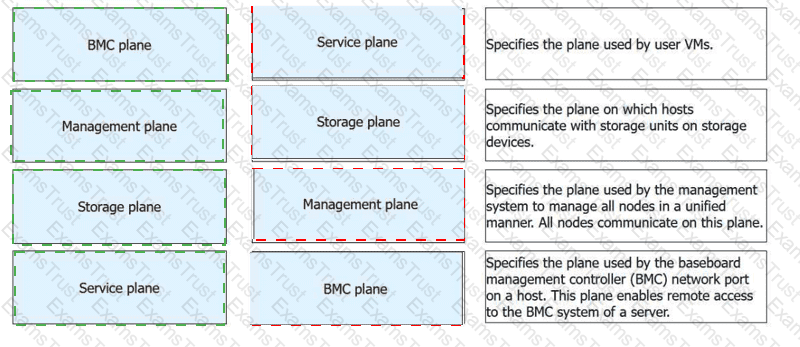
1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
In the Huawei FusionCompute architecture, network traffic is logically divided into specialized "planes" to ensure security, isolation, and optimal performance. TheBMC plane(Baseboard Management Controller) is dedicated to hardware-level management. It utilizes a dedicated network port on the physical host toenable remote access to the BMC system, allowing administrators to perform out-of-band tasks such as power control, BIOS configuration, and hardware health monitoring regardless of the OS state.
TheManagement planeis the communication backbone for the virtualization platform. It is used by the Virtual Resource Management (VRM) and Computing Node Agent (CNA) tomanage all nodes in a unified manner. All nodes in the cluster communicate on this plane to report resource status and receive management instructions. TheStorage planeis specifically reserved for data transmission between the compute hosts and the back-end storage infrastructure. This is theplane on which hosts communicate with storage units(such as LUNs or shared folders) to handle VM disk I/O.
TheService planeis the network segmentused by user VMsfor their actual service traffic. It carries the data produced and consumed by the applications running inside the virtual machines. Huawei documentation mandates the isolation of these planes—typically via VLANs—to prevent a "broadcast storm" or high data load in one plane (like Storage) from impacting the accessibility of the Management plane or the performance of user services.
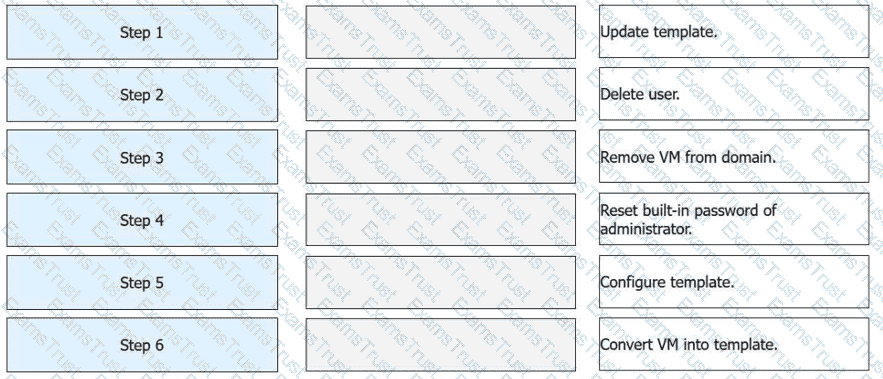
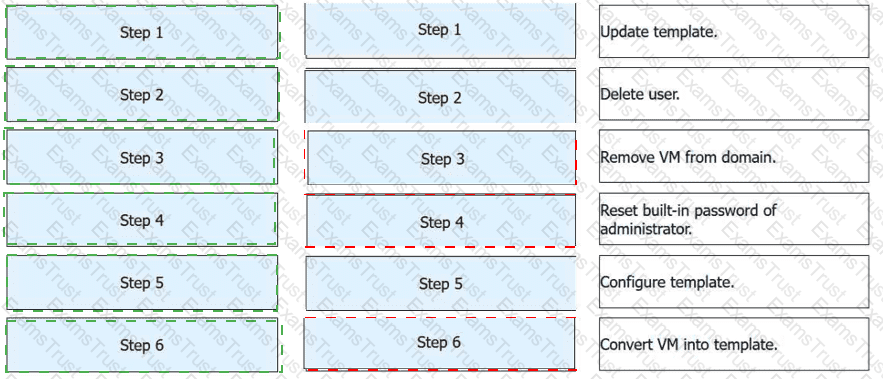
FusionAccess can use a provisioned full copy VM as a full copy VM template. Place the following operations in the correct order.
Step
Operation
Step 1
Update template.
Step 2
Delete user.
Step 3
Remove VM from domain.
Step 4
Reset built-in password of administrator.
Step 5
Configure template.
Step 6
Convert VM into template.
Step
Operation
Technical Rationale
Step 1
Update template
Power on the VM to install the latest OS patches and software updates.
Step 2
Delete user
Remove user profiles and personal data to ensure the master image is clean.
Step 3
Remove VM from domain
Disjoin the VM from the AD domain to prevent Security Identifier (SID) or account name conflicts on new clones.
Step 4
Reset built-in administrator password
Set a secure, standardized baseline credential for the local administrator account.
Step 5
Configure template
Run theHuawei Desktop Preparation Toolto optimize the OS and encapsulate the system.
Step 6
Convert VM into template
Use the management console to officially mark the VM as a read-only template resource.
Initialization (Steps 1-4):Before a VM can be turned into a "Golden Image," it must be stripped of its unique identity. This includes removing it from anyActive Directory (AD)domain and clearing out specific user accounts. Failing to remove the VM from the domain can lead to "duplicate computer name" errors when new desktops are provisioned from the final template.
System Encapsulation (Step 5):The "Configure template" phase is often synonymous withSysprepor the Huawei-specific encapsulation process. This step resets the OS clock and generalizations, such as the hardware-dependent drivers, so the image can boot correctly on any host in the cluster.
Finalization (Step 6):Once converted into a template, the VM is no longer a running instance. It becomes a master file that theITA (IT Adapter)uses for rapid service provisioning.
According to the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing documentation, converting a provisioned full-copy virtual machine (VM) back into a template is a specific administrative workflow used for updating "Golden Images" without starting from a bare VM. The process must follow a logical sequence to ensure that the final template is clean, generalized, and compatible with the FusionAccess management plane.
The workflow begins withStep 1: Update template, which involves powering on the VM to install necessary software patches, security updates, or new applications. Once updated,Step 2: Delete useris performed to remove any cached user profiles, temporary files, or local user data that should not exist in the master image.Step 3: Remove VM from domainis a critical step to ensure that the VM is no longer associated with a specific Active Directory security identifier (SID) or domain account, preventing SID conflicts when the template is later used to provision multiple new desktops.
Following the domain disjunction,Step 4: Reset built-in password of administratoris required to ensure the FusionAccess system can maintain management access via a known, local credential during the subsequent automation phases.Step 5: Configure templateinvolves running theHuawei Desktop Preparation Tool. This tool performs system encapsulation (similar to Sysprep), optimizes the OS for VDI usage, and prepares the Huawei Desktop Agent (HDA). Finally,Step 6: Convert VM into templateis the final action performed in the FusionCompute or FusionAccess management console. This marks the VM as a read-only template resource, ready to be used by the ITA (IT Adapter) for rapid service provisioning.
Which of the following technologies is used by Open vSwitch (OVS) for remote access and traffic control?
OpenFlow
Open vSwitch database (OVSDB)
Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD)
Network quality analysis (NQA)
In the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, specifically under the "Network Technology Basics" module, Open vSwitch (OVS) is introduced as a key component of software-defined networking (SDN). The primary technology used by OVS for remote access to its control plane and for the programmatic control of traffic flows is OpenFlow.5 OpenFlow is a standard communications protocol that allows an SDN controller (the "brain" of the network) to interact with the forwarding plane (the switch) of a network device.
OpenFlow enables "traffic control" by allowing the controller to define specificflow rules.6These rules tell the switch exactly how to handle packets based on various criteria such as source MAC, destination IP, or TCP port. Instead of the switch making local, autonomous decisions (as a traditional switch does), OVS uses OpenFlow to receive instructions from a centralized management layer. This is how Huawei’s cloud infrastructure achieves "remote access" for network orchestration; an administrator can change the network behavior of thousands of virtual machines across multiple physical hosts by pushing new OpenFlow tables from a central controller.
WhileOVSDB(Option B) is also a critical protocol for OVS, its primary role is to manage theconfigurationof the switch (such as creating bridges, adding ports, or setting up tunnels), rather than the "traffic control" or "flow steering" handled by OpenFlow.BFD(Option C) is used for link failure detection, andNQA(Option D) is a Huawei-specific tool for measuring network performance. In the context of the HCIA exam, OpenFlow is the correct answer for the protocol that enables the intelligent, remote management of data paths in a virtualized network environment.
====================
In FusionCompute, the user can set the priority for each member port in a port group.
TRUE
FALSE
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training materials, the statement is FALSE. In a Distributed Virtual Switch (DVS), a port group is a management object used to define common attributes for a collection of virtual ports. These attributes include VLAN settings, security policies, and Quality of Service (QoS) parameters. When an administrator configures a priority (such as an 802.1p priority tag) within a port group, that configuration applies to the entire port group, meaning all VMs connected to that group share the same policy.
The system does not allow for the setting of individual "priorities" for each specific member port (VM port) directly within the port group configuration. Instead, the port group ensures consistency across the virtual network. If different VMs required different priorities, they would typically be placed into different port groups, each with its own specific QoS and VLAN configuration.
It is important to distinguish this fromUplink Groups. In an uplink group (which connects the DVS to physical network cards), administratorscanset priorities or active/standby states for physical member ports (NICs) to control traffic flow and redundancy. However, for the virtual ports used by VMs within a standard port group, the logic is based on uniform policy enforcement. Huawei's documentation emphasizes that port groups are designed to simplify management by allowing the administrator to configure a policy once and have it apply to all associated VM NICs, thereby reducing the risk of manual configuration errors on a per-port basis.
====================
Which of the following statements about VM group types and related operations during virtual desktop provisioning on FusionAccess is false?
If the desktop group type is Static Pool, linked clone and full copy VMs can be provisioned.
During quick provisioning of virtual desktops, administrators can assign desktops of different types to different users.
During virtual desktop creation, the system cannot add the virtual desktop to a specified VM group until virtual desktop assignment.
If the desktop group type is Dynamic Pool, linked clone and full copy VMs can be provisioned.
FusionAccess supports different desktop pool types, each with specific provisioning rules:
Static Pool supports both linked clone and full copy desktops → A is true.
Quick provisioning allows flexible desktop assignment strategies → B is true.
VM grouping is finalized during desktop assignment → C is true.
Dynamic Pool typically supports linked clone desktops only, because desktops are created and destroyed dynamically.
Therefore, statement D is false.
Which of the following technologies cannot be used to manage networks?
Distributed virtual switch (DVS)
Snapshot
Virtual NIC
Network I/O control
In the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, network management and storage management are distinct functional areas. The technologies listed in options A, C, and D are all integral to the networking stack of a virtualized environment. A Distributed Virtual Switch (DVS) is used to manage the logical network across multiple physical hosts.1 A Virtual NIC (vNIC) is the virtualized network interface that provides connectivity for a Virtual Machine.2 Network I/O Control is a feature used to manage and prioritize network traffic bandwidth (Quality of Service) to ensure that critical services receive the necessary throughput.3
However, aSnapshotis strictly a data management and protection technology, not a networking tool.4According to the official training materials, a snapshot records the status of a Virtual Machine's data (specifically its virtual disks and, optionally, its memory state) at a specific point in time.5This allows an administrator to "roll back" the VM to a previous state in case of software failure, a botched update, or data corruption.6While a snapshot captures theconfigurationof the network settings that existed at that time, it does not "manage" the network itself. It does not handle frame forwarding, VLAN tagging, or traffic shaping.
In the context ofFusionCompute, snapshots are managed at the storage layer (VIMS or local storage). They are used for disaster recovery and testing. Using a snapshot to attempt network management would be a fundamental misunderstanding of the architecture. Therefore, within the HCIA framework, students must distinguish between "Connectivity/Control" (Networking) and "Persistence/State" (Storage/Snapshots). This distinction ensures that administrators apply the correct tools for specific operational tasks, such as using the DVS for traffic isolation and snapshots for data backup.
====================
Which of the following statements aretrueabout distributed storage?
Distributed storage features outstanding scalability.
Distributed storage typically uses general-purpose servers rather than storage devices.
Distributed storage leverages RAID technology to ensure high data availability and security.
Distributed storage has no controller enclosure or disk enclosure. All disk storage resources are delivered by general-purpose servers.
Distributed storage is a core concept in cloud computing and is emphasized in HCIA–Cloud Computing as a foundational technology for large-scale cloud platforms.
OptionAis true. Distributed storage is designed forhorizontal scalability, allowing storage capacity and performance to increase simply by adding more nodes.
OptionBis true. Unlike traditional centralized storage systems, distributed storage typically runs ongeneral-purpose x86 servers, reducing cost and improving flexibility.
OptionCis false. Distributed storagedoes not rely on traditional RAIDfor data protection. Instead, it usesdata replication or erasure coding, which are more suitable for large-scale distributed environments.
OptionDis true. Distributed storage eliminates the need for dedicated controller enclosures or disk enclosures. Storage resources are directly provided bygeneral-purpose servers, which aligns with cloud-native architecture principles described in HCIA materials.
When a VM template is created on FusionAccess, select“Configure user login”if the_____group members want to log in to the VM.
(Enter the correct word on the GUI)
AD
In Huawei FusionAccess, user authentication and authorization for Windows desktops are typically integrated withActive Directory (AD). During VM template creation, the option“Configure user login”is used to specify who is allowed to log in to the virtual desktop.
According to the HCIA–Cloud Computing FusionAccess service provisioning process, this option is selected whenAD group membersare intended to access the VM. FusionAccess then uses AD-based authentication to control desktop login permissions, ensuring centralized identity management and consistent security policies.
Therefore, the correct word shown on the GUI and required to complete the sentence isAD.
Which of the following statements isfalseabout Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)?
RAID 0 uses striping to improve data read and write performance.
RAID 6 uses mirroring to ensure user data reliability.
RAID 1 uses mirroring to ensure user data reliability.
RAID 5 uses parity check to ensure data reliability.
RAID technology is a key topic in theStorage Technology Basicsdomain of HCIA–Cloud Computing. Different RAID levels provide varying balances of performance, capacity, and fault tolerance.
RAID 0 (A)uses data striping across multiple disks to improve read/write performance but providesno data redundancy. This statement is correct.
RAID 1 (C)usesdisk mirroring, where identical data is written to two disks, ensuring high data reliability. This statement is correct.
RAID 5 (D)usesdistributed parityacross disks, allowing data recovery if one disk fails. This is also correct.
RAID 6 (B)is the false statement. RAID 6 doesnotuse mirroring. Instead, it usesdual parity, allowing the system to tolerate the failure oftwo disks simultaneously.
Therefore, optionBis incorrect and is the false statement.
The following table lists the FusionAccess environment plan. Which of the following network segments is the most suitable for deploying FusionAccess Linux infrastructure VMs?
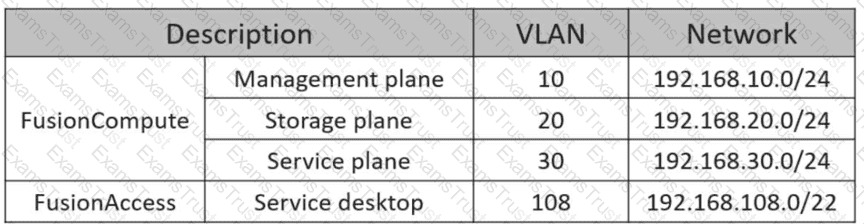
192.168.108.0/22
192.168.10.0/24
192.168.30.0/24
192.168.20.0/24
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing documentation, specifically within the "Planning and Deployment of FusionAccess" module, the network architecture of a cloud data center is divided into distinct planes to ensure security, isolation, and efficient management. In a FusionAccess deployment, infrastructure virtual machines (VMs)—which include critical components such as the ITA (IT Adapter), HDC (Huawei Desktop Controller), WI (Web Interface), and the GaussDB database—are considered the "management brain" of the desktop cloud solution.
TheManagement planeis specifically designed to facilitate communication between management systems and all nodes within the cloud environment. In the provided scenario, the network segment192.168.10.0/24(VLAN 10) is designated as the FusionCompute Management plane. Huawei's official best practices dictate that Linux infrastructure VMs must be deployed on this plane to allow them to communicate directly with theVirtual Resource Management (VRM)node and theComputing Node Agent (CNA)hosts. This placement ensures that management traffic for desktop provisioning and resource orchestration remains isolated from general user traffic and heavy storage data flows.
In contrast, theService plane(192.168.30.0/24) is intended for the traffic of standard user applications, while theService desktopsegment (192.168.108.0/22) is reserved for the end-user virtual desktops themselves. Placing infrastructure VMs on theStorage plane(192.168.20.0/24) would be technically incorrect, as it is strictly dedicated to disk I/O and would not provide the necessary logical path to the management portal. Therefore, selecting network segment B ensures that infrastructure components are securely positioned to manage the desktop lifecycle while maintaining high availability and administrative accessibility.
Match the emerging technologies with their respective features or application scenarios
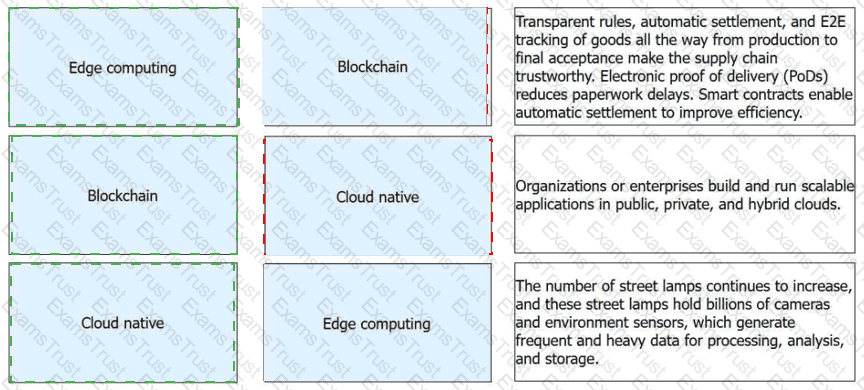
Emerging Technology
Feature / Application Scenario
Edge computing
The number of street lamps continues to increase, and these street lamps hold billions of cameras and environment sensors, which generate frequent and heavy data for processing, analysis, and storage.
Blockchain
Transparent rules, automatic settlement, and E2E tracking of goods all the way from production to final acceptance make the supply chain trustworthy. Electronic proof of delivery (PoDs) reduces paperwork delays. Smart contracts enable automatic settlement to improve efficiency.
Cloud native
Organizations or enterprises build and run scalable applications in public, private, and hybrid clouds.
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, emerging technologies like Edge Computing, Blockchain, and Cloud Native are reshaping modern IT infrastructures to handle data more efficiently and securely. In the context ofEdge Computing, the massive proliferation of IoT devices in smart cities—such as billions of cameras and environmental sensors mounted on street lamps—creates a data influx that traditional centralized clouds cannot process in real time without significant latency. Edge computing solves this by moving processing and storage capabilities physically closer to the data sources, allowing for nearly instantaneous response times for critical urban systems like traffic management and public surveillance.
Blockchaintechnology provides a decentralized, distributed ledger that is transformative for global supply chain management. By creating a "single source of truth" that is transparent and immutable, it enables end-to-end (E2E) tracking of goods from production to the final consumer. A core feature is the use ofsmart contracts, which are automated, self-executing rules that trigger settlements and payments immediately upon meeting conditions like electronic proof of delivery (PoD), thereby eliminating intermediaries and reducing paperwork delays.
Finally,Cloud Nativerepresents an architectural approach designed to fully exploit the cloud computing model. The official definition from the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) states that these technologies "empower organizations to build and run scalable applications in modern, dynamic environments such as public, private, and hybrid clouds". By utilizing independent microservices and portable containers, cloud-native applications achieve the high availability, elasticity, and rapid deployment speed required to meet evolving business needs across diverse infrastructure types.
In FusionCompute, which of the following statements are false about security groups?
Similar to firewalls, security groups use iptables to filter packets for access control.
A running VM can be added to a security group.
If VM A is added to security group B, it cannot be added to other security groups.
Users can create security groups on VMs and add security group rules.
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing documentation, security groups act as a distributed virtual firewall for Virtual Machines (VMs). Statement C is FALSE because FusionCompute allows a single Virtual Machine (or more specifically, a virtual NIC) to belong to multiple security groups simultaneously. This multi-group association allows for tiered security policies, such as having one security group for general web traffic and another for specific management access. When a VM belongs to multiple groups, the rules from all groups are aggregated to determine the final access control list.
Statement D is alsoFALSEbecause of the terminology regarding the "creation" location. In the FusionCompute architecture, security groups are logical objects created and managed within theVRM (Virtual Resource Management)portal, not "on the VMs" themselves. A security group exists independently of any specific VM; administrators create the group and define its rules first, and then they associate VMs with that group. Furthermore, users do not add rules "on VMs"; they add rules to the security group object in the management plane, which the system then automatically pushes to the corresponding CNA hosts where the VMs are running.
The other statements are technically accurate. Statement A is correct as Huawei’s security groups utilize the underlying LinuxiptablesorOVS (Open vSwitch)flow rules to filter packets at the hypervisor level. Statement B is also true; a VM's security group membership can be modified dynamically while the VM is in a running state without requiring a restart or causing a service interruption. This flexibility is a key feature of Huawei’s software-defined networking, allowing for real-time security adjustments in a dynamic cloud environment.
====================
Match the following virtualization technologies with their descriptions.
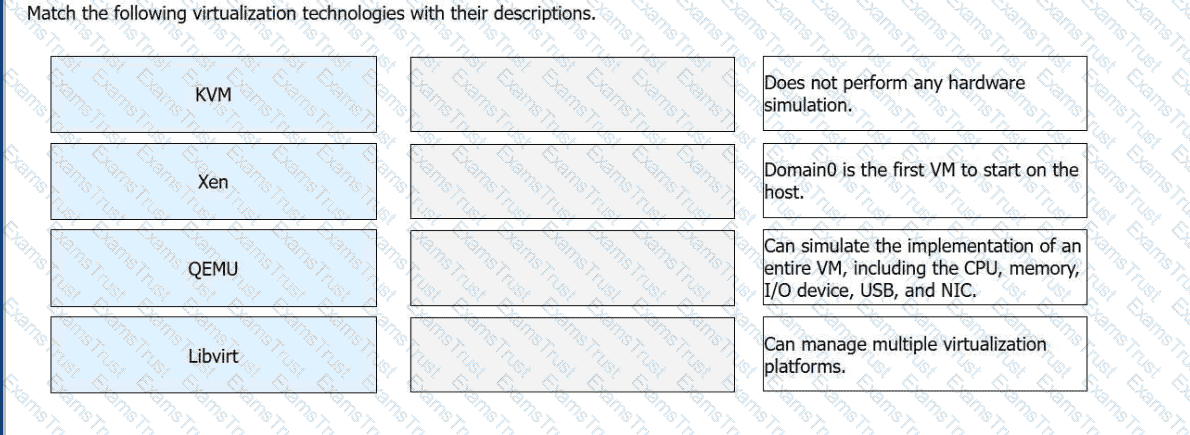
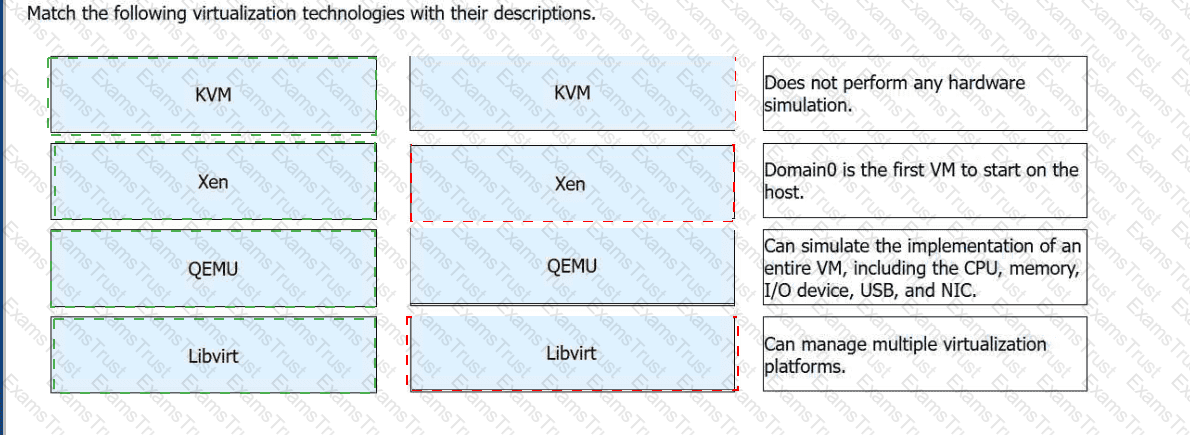
Virtualization Technology
Description
KVM
Does not perform any hardware simulation.
Xen
Domain0 is the first VM to start on the host.
QEMU
Can simulate the implementation of an entire VM, including the CPU, memory, I/O device, USB, and NIC.
Libvirt
Can manage multiple virtualization platforms.
Huawei's technical materials differentiate between these technologies based on their specific roles within the virtualization ecosystem.KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)is an open-source module within the Linux kernel. While it provides the core virtualization capabilities for CPU and memory, it is defined in the HCIA curriculum as a technology thatdoes not perform hardware simulationitself. Instead, it typically relies on hardware-assisted virtualization or integrates with other tools to handle I/O operations.
Xenis a Type-1 hypervisor that operates directly on the hardware. A unique feature of the Xen architecture isDomain0, which is a privileged virtual machine that starts first and provides the management environment and drivers for other guest VMs (DomainU). In contrast,QEMUis a pure software-based emulator. It is powerful because itcan simulate an entire VM, including all peripherals like the CPU, NIC, and USB. However, because it relies on software simulation, its performance is lower than hardware-assisted technologies unless it is used as a backend for KVM.
Finally,Libvirtserves as the universal management layer. It is a set of open-source library functions and APIs that allow administrators tomanage multiple virtualization platforms(including KVM, Xen, and VMware) using a standardized command set. It provides transparency to upper-layer management software by abstracting the complexities of the underlying hypervisor. Understanding how these technologies interact—such as KVM utilizing Libvirt for management and QEMU for I/O—is a critical learning objective for candidates preparing for the Huawei H13-511 exam.
Which of the following statements about the differences betweenuser groupsandorganizational units (OUs)aretrue?
OUs and user groups are Active Directory objects.
An OU can contain objects such as accounts, computers, printers, and shared folders.
Group policies can be configured for both OUs and user groups.
A user group can only contain accounts.
In AD,OUsanduser groupsare both used for organizing and managing resources, but they differ in function.
Ais true. Both OUs and user groups areAD objects.
Bis true. An OU can contain multiple types of AD objects, includingusers, computers, printers, and shared resources.
Cis false.Group policies cannot be directly applied to user groups; they are applied to domains, sites, or OUs.
Dis false. A user group can containusers, computers, and even other groups, not only user accounts.
Thus, the correct answers areA and B.
Cloud-native technologies enable organizations to build and run scalable applications in public, private, or hybrid cloud environments. Which of the following isnota representative cloud-native technology?
Service mesh
Virtualization
Microservice
Container
Cloud-native architecture emphasizesapplication-level design and management, focusing on agility, scalability, and resilience.
Microservices,containers, andservice meshesare core cloud-native technologies.
Virtualizationis a foundational cloud technology but belongs totraditional cloud infrastructure, not cloud-native application architecture.
Therefore, the correct answer isVirtualization.
Which of the following statements about the differences between a domain and an OU are true?
Users can log in to a domain but not to an OU.
Group policies can be configured for both OUs and domains.
An OU can exist in a domain, and a domain can also exist in an OU.
Both OUs and domains can contain AD objects.
In the context of FusionAccess deployment, understanding Microsoft Active Directory (AD) is critical. According to the official Huawei curriculum, a Domain and an Organizational Unit (OU) serve different purposes in a network hierarchy. Statement A is TRUE because a domain is a security and administrative boundary; users authenticate "to the domain." An OU is merely a logical container inside that domain used for organization; it does not function as an authentication boundary itself.
Statement B isTRUE. Group Policy Objects (GPOs) are the primary tool for managing desktop settings in a Huawei VDI environment. GPOs can be linked at the Domain level (applying to everyone) or at the OU level (applying only to the users or computers within that specific folder). This allows FusionAccess administrators to apply specific security rules—such as disabling USB ports or setting custom wallpapers—to one department (one OU) without affecting the entire company.
Statement D is alsoTRUE. Both entities are containers for AD objects such as User accounts, Computer accounts, and Security Groups. However, statement C isFALSE. While an OU always existsinsidea domain (to organize that domain's objects), a domaincannotexist inside an OU. Domains exist within a Forest or Tree structure.2This distinction is vital for HCIA candidates because the FusionAccessITA (IT Adapter)requires a specific OU structure to be pre-created (e.g., an OU for Desktops and an OU for Users) to properly apply the automated provisioning and management policies that define the desktop cloud environment.
====================
FusionCompute adopts hardware-assisted virtualization technology to reduce memory virtualization overhead.
TRUE
FALSE
Huawei FusionCompute leverageshardware-assisted virtualization technologiessuch asIntel VT-x, EPT, and AMD-V, which significantly reduce the overhead associated with CPU and memory virtualization.
Memory virtualization traditionally involved complex software-based address translation, which introduced performance overhead. With hardware-assisted features such asExtended Page Tables (EPT), memory mapping is handled directly by the CPU, improving efficiency and performance.
This approach is explicitly highlighted in HCIA–Cloud Computing materials as a key reason why FusionCompute delivers near-native performance for virtual machines.
Therefore, the statement isTRUE.
Common storage networks include direct attached storage (DAS), network attached storage (NAS), and storage area network (SAN). SANs are divided into Fibre Channel storage area networks (FC SANs) and IP storage area networks (IP SANs).
TRUE
FALSE
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing technical guidelines, storage is categorized by its connection method and the protocol used to access data. Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is the most basic form, where storage devices are connected directly to a single server via an internal bus or external cable. While simple, it lacks the scalability and resource-sharing capabilities required for modern cloud data centers. Network Attached Storage (NAS) provides file-level access over a standard IP network, typically using protocols like NFS or CIFS, allowing multiple clients to share a central pool of files over a local area network.
The Storage Area Network (SAN) is a specialized, high-speed network that provides block-level access to storage, making it appear to the operating system as a locally attached disk. In Huawei’s virtualization solutions, SANs are the preferred choice for high-performance clusters and features like VM Live Migration. As the statement correctly identifies, SANs are primarily divided into two types based on the transport protocol used: Fibre Channel (FC) SANs and IP SANs. FC SANs utilize dedicated fiber-optic cables, FC switches, and Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) to transmit data using the Fibre Channel protocol, offering extremely high reliability and minimal latency. Conversely, IP SANs utilize standard Ethernet infrastructure and the iSCSI protocol to encapsulate SCSI commands into IP packets. This allows for lower costs and easier management by leveraging existing Ethernet knowledge. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for the HCIA exam, as the choice between FC and IP SAN directly impacts the deployment architecture and performance characteristics of Huawei's FusionCompute and FusionAccess solutions in an enterprise environment.
Copyright © 2014-2026 Examstrust. All Rights Reserved
