A SOC team using Cisco security technologies wants to distinguishIndicators of Attack (IOAs)fromIndicators of Compromise (IOCs)during threat hunting. Which scenario BEST represents an IOA rather than an IOC?
A threat hunting team wants to ensure hunts are repeatable, scalable, and less dependent on individual analyst intuition. What is the MOST important process improvement?
A threat hunting team is attempting to attribute a series of intrusions across multiple organizations to a known threat actor. The malware binaries differ across incidents, infrastructure changes frequently, and IP addresses rotate daily. Which evidence provides the STRONGEST basis for confident attribution?
A threat hunter is asked to model how an attacker could abuse cloud identity misconfigurations to escalate privileges without exploiting software vulnerabilities. Which modeling approach BEST supports this analysis?
Refer to the exhibit.
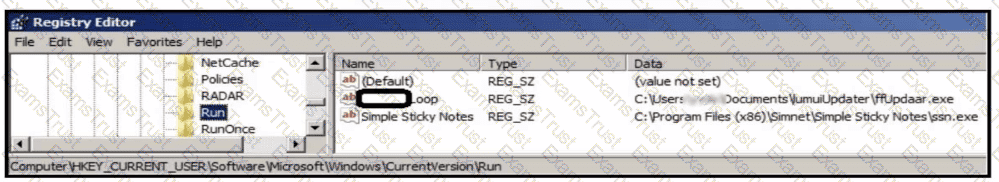
An analyst is evaluating artifacts and logs collected from recent breach. In the logs, ATP established persistency of malware by placing a path to the executable in a specific registry entry. What is the difference between the ATP's approach and using HKEY LOCAL MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run instead?
Refer to the exhibit.
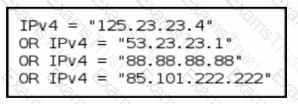
A threat-hunting team makes an EDR query to detect possible C2 outbound communication across all endpoints. Which level of the Pyramid of Pain is being used?
A threat hunter wants to detect fileless malware activity usingCisco Secure Endpoint. Which behavior would MOST strongly indicate fileless execution?
The security team detects an alert regarding a potentially malicious file namedFinancial_Data_526280622.pdfdownloaded by a user. Upon reviewing SIEM logs and Cisco Secure Endpoint, the team confirms that the file was obtained from an untrusted website. The hash analysis of the file returns an unknown status. Which action must be done next?
During multiple intrusions, analysts observe that attackers consistently perform internal reconnaissance before privilege escalation, avoid noisy exploitation, and limit actions to business hours of the victim’s region. Why is this observation important for attribution?

Refer to the exhibit. Which technique is used by the attacker?
A threat hunter usesCisco Secure Network Analytics (Stealthwatch)to identify potential command-and-control traffic. Which characteristic MOST strongly indicates beaconing behavior?
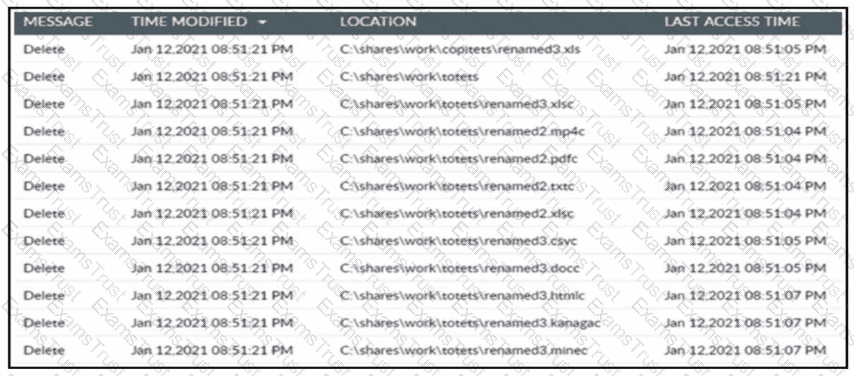
Refer to the exhibit. A cybersecurity team receives an alert from its Intrusion Prevention System about multiple file changes to a file server. Before the changes were made, the team detected a successful remote sign-in from a user account to the server. Which type of threat occurred?
A threat hunter completes a structured hunt and confirms malicious lateral movement within the environment. Which action BEST ensures the hunt contributes to long-term defensive improvement?
Refer to the exhibit.

A security team detects a spike in traffic from the company web server. After further investigation, the team discovered that multiple connections have been established from the server to different IP addresses, but the web server logs contain both expected traffic and DDoS traffic. Which attribute must the team use to further filter the logs?
A security analyst receives an alert that host A, which has an IP address of 192.168.5.39, has a new browser extension installed. During an investigation of the SIEM tool logs, the analyst discovers that host A made continuous TCP connections to an IP address of 1.25.241.8 via TCP port 80. The 1.25.241.8 IP address is categorized as a C2 server. Which action should the analyst take to mitigate similar connections in the future?
Refer to the exhibit.

A company recently was breached and decided to improve their security posture going forward. A security assessment was ordered, specifically intended to test weak points exploited during the breach. A security analyst reviews server logs to identify activities related to the aforementioned security assessment. Which entry suggests a delivery method associated with authorized assessment?
A SOC manager wants to evaluate whether the organization’s Cisco-based threat hunting program is improving over time. Which metric BEST reflects increased threat hunting effectiveness?
A Cisco-focused SOC wants to move detection coverage higher on thePyramid of Pain. Which hunting outcome BEST supports this objective?