Which technique averages individual frames together to improve the image?
Which factor determines elevational resolution?
What is the primary determining factor of the fundamental frequency for pulsed wave transducers?
How is the wavelength affected when switching from a 10 MHz transducer to a 5 MHz transducer?
Decreasing which parameter will improve axial resolution?
Which function should be decreased in order to minimize potential bioeffects?
Which settings will lead to the highest temporal resolution?
What is required when interrogating higher blood velocities at angles closer to zero degrees?
Which color Doppler control allows for reassignment of red and blue to represent flow direction?
In addition to velocity, which factor affects acoustic impedance?
Which spectral Doppler finding can occur when using a low pulse repetition frequency setting?
What is the result of increased transducer damping?
What produces increased attenuation within soft tissue?
Which change improves temporal resolution during color flow imaging?
Which gray-scale artifact occurs when a structure attenuates less than the adjacent tissues?
Which settings would produce the best temporal resolution?
What information does the ultrasound system calculate to display color flow?
How is variable transmit focus with a linear phased array accomplished?
How can spectral Doppler cross talk be reduced?
What device is used to determine axial resolution?
What is the relationship between overall gain and image brightness?
What causes color flash artifact?
During 3-D volume acquisition, the quality of the images is most dependent upon which factor?
What is effected by increasing the color scale?
Which artifact causes a simple cyst to appear to contain debris?
Which resolution can be evaluated in the area indicated by the red oval in this image of a tissue-equivalent phantom?
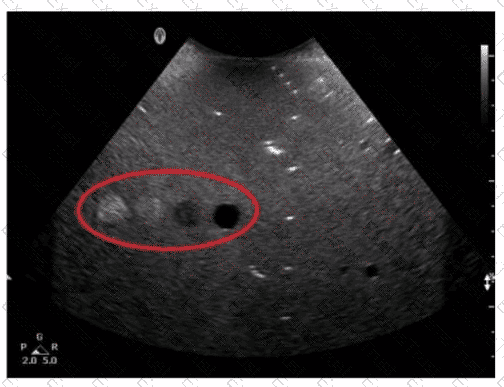
Which resolution capability is most affected by spatial pulse length?
Which pulsed-wave Doppler adjustment would be appropriate to correct the aliasing seen in this image?
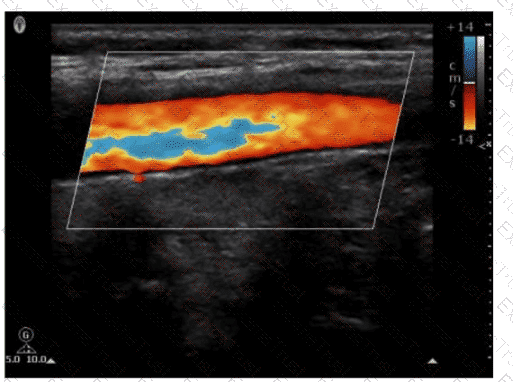
What is the effect of increasing the sample volume on the spectral Doppler signal tracing?
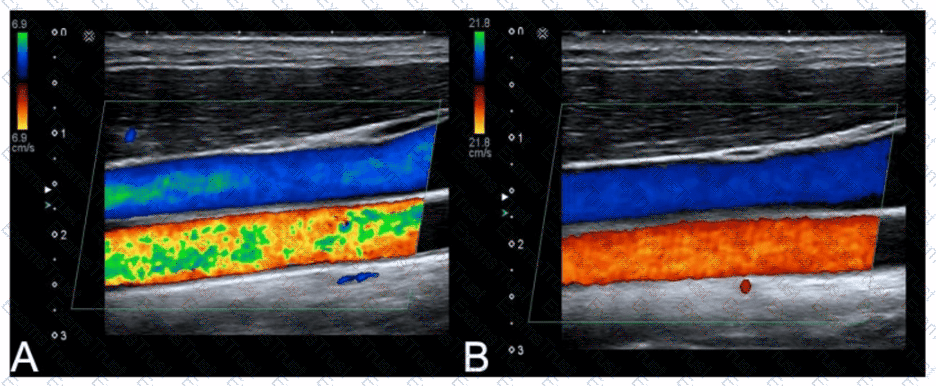
Which adjustment resulted in the change from image A to image B?
Which pulsed-wave Doppler adjustment would be appropriate to correct the aliasing seen in this image?
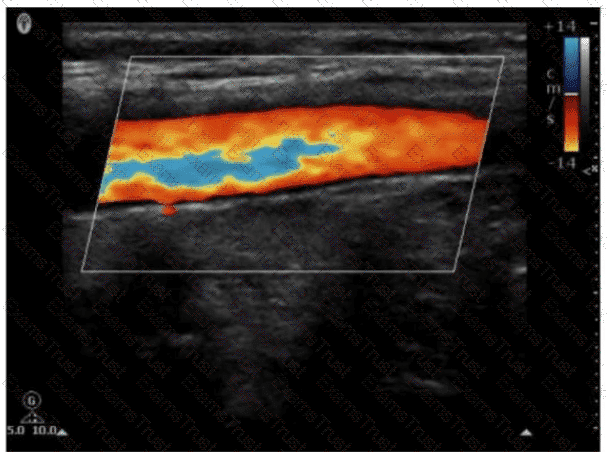
Which resolution is improved by focusing?
What method can be used to resolve aliasing artifact?
Which adjustment resolves spectral Doppler aliasing?
Which technique averages image frames over time to reduce noise?
What causes increased echogenicity distal to an anechoic structure?
What is the function of M-mode?
Which factor will improve axial resolution?
What is the term for an ultrasound system's ability to display low-level echoes?
What is the term for the change in direction of a sound wave crossing a tissue boundary at an oblique angle?
Which artifact is caused by defects in the crystals of the transducer?
What is the result of increasing the wall filter setting during Doppler sampling?
During a color Doppler scan, which angle to flow would most likely result in no color being visualized?
If the pulse repetition frequency is 3 kHz, what is the maximum Doppler shift that can be detected without aliasing?
What does damping in a pulsed-wave transducer affect?
Which function is the purpose of the matching layer?
Which action is the first step for the removal of visible contaminants from the transducer?
In this image, what does the data below the baseline represent?
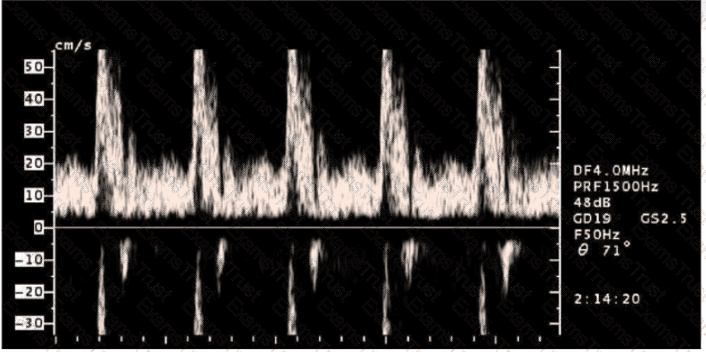
What is the most effective way to reduce aliasing on color Doppler?
Which target group in this image of a tissue-mimicking phantom is used to evaluate axial resolution?
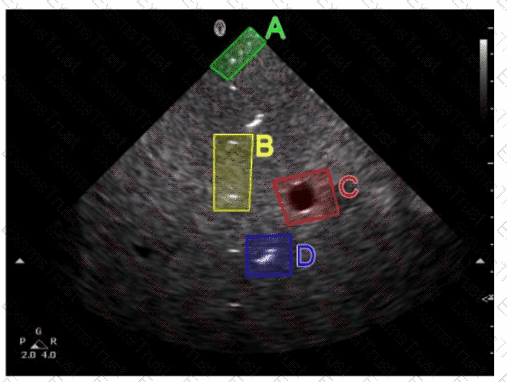
What is a potential negative consequence of using a high wall filter?
Which setting improves temporal resolution?
Which adjustment will reduce the artifact in the cystic lesion in image A resulting in image B?
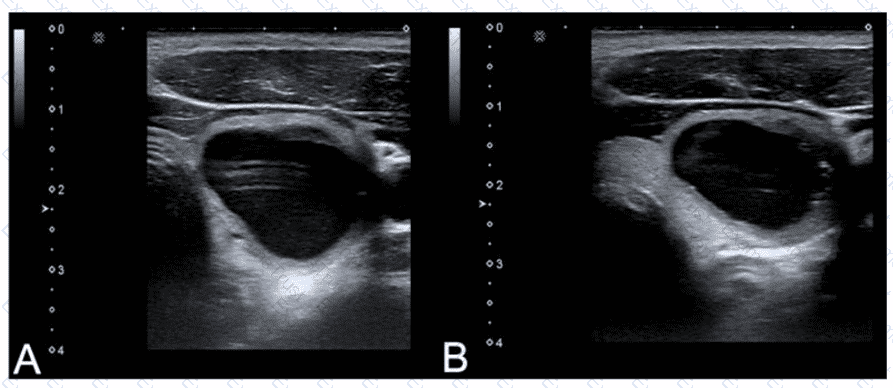
Which parameters determine the propagation speed of sound in a medium?
What is true regarding the display for color Doppler?
What parameter change reduces spectral Doppler aliasing?