A continuous flow murmur is most likely due to which abnormality?
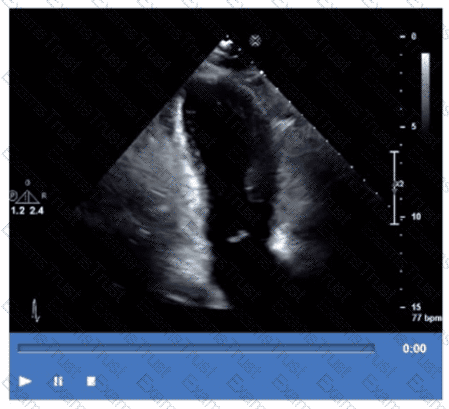
Which coronary artery territory is associated with the wall motion abnormality demonstrated in this video?
Which hepatic vein flow pattern signals severe tricuspid regurgitation?
Which Doppler signal is used to calculate the pulmonary artery end-diastolic pressure gradient?
A patient with a ventricular septal defect, an atrial septal defect, and a cleft mitral valve is likely to have which abnormality?
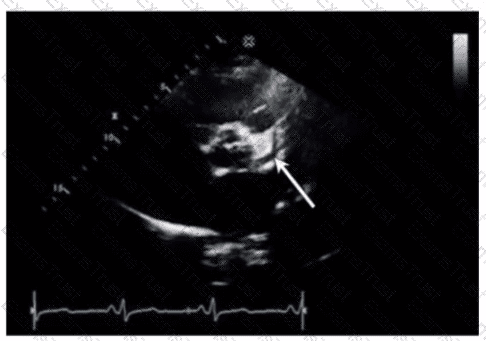
What is indicated by the arrow on this video clip?
Which of the following can be calculated from the peak tricuspid regurgitant velocity?
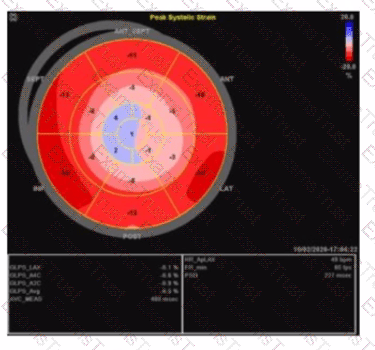
Which pathology is consistent with the left ventricular strain pattern shown in this image?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does mitral valve prolapse occur?
In which view is the superior vena cava visualized in its long axis?
Which method is appropriate for measuring the left atrial diameter in parasternal long axis?
Which maneuver aids in uncovering potential diastolic dysfunction while performing pulsed wave Doppler of the mitral valve?
Which unit of measurement is used to quantify tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion?
Which type of mass is typically attached to the fossa ovalis of the left atrium?
What is the normal dP/dt value of left ventricular systolic function?
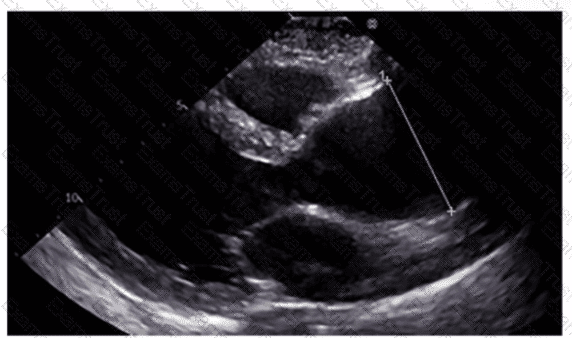
Which region of the aorta is being measured to assess the critical finding in this image?
Which of the following does the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure estimate?
What minimum number of poorly-visualized contiguous left ventricular (i_V) regional wall segments indicate the use of contrast agents for LV endocardial border definition?
Which type of defect can be seen in this video clip?
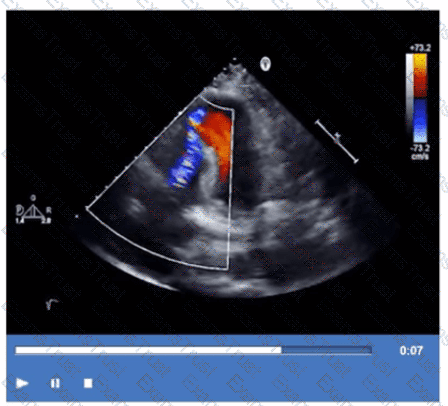
Which adjustment should be made to optimize this video?
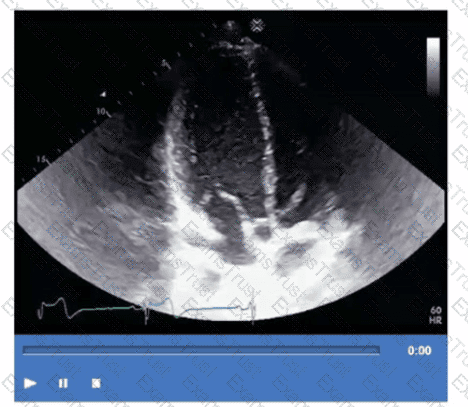
When should the left ventricular end-diastohc diameter be measured?
Which Doppler signal is most consistent with significant aortic valve regurgitation?
The 'P' wave of an electrocardiogram relates to which echocardiography event?
A patient presents with tender, red lesions on their fingers and toes (Osier nodes). Which finding is most likely?
What can be concluded about the tricuspid valve demonstrated in this image?
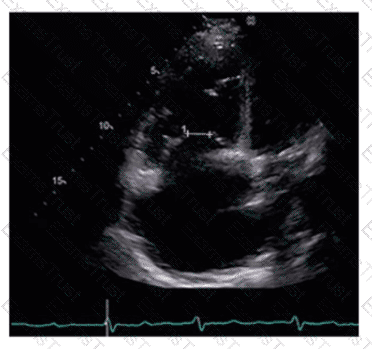
Which statement is considered true regarding tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE)?
Which mitral valve filling pattern is characterized by a long deceleration time and an E/A ratio of 0.6?
The parasternal long axis view can be used to visualize which anatomical structure?
Which of the following occurs during the strain phase of the Valsalva maneuver?
Which of the following is a feature of constrictive pericarditis?
In patients with interrupted aortic arch, which structure allows Wood to flow into the descending aorta?
What is the route of ventricular depolarization?
Which measurement is indicated by the arrow on this image?
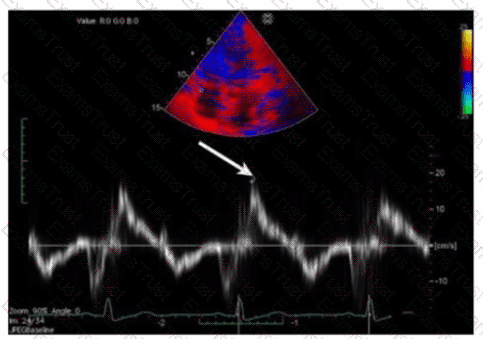
Which type of valvular lesion most commonly requires further evaluation with a non-imaging transducer?
Acute severe aortic regurgitation leads to a marked increase in which pressure?
Which sonographic views allow visualization of a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)?
Left atrial dilation, concentric left ventricular hypertrophy, and aortic root dilation are echocardiography findings commonly associated with which condition?
Which flow component is indicated by the arrows on this image?
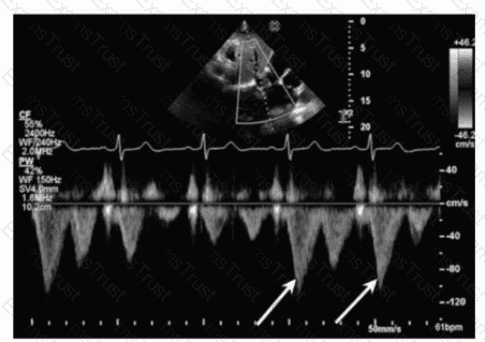
Which wall is indicated by the arrow on this image?
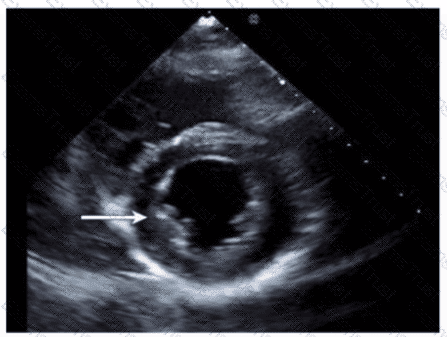
Which diagnosis is most likely confirmed by echocardiography in a 65-year-old female presenting with new onset chest pain associated with ST segment elevation on the electrocardiogram and angiographically normal coronary artenes?
Which coronary artery is identified by the arrow on this image?