The following statements are about 501(c)(9) trusts. Select the answer choice containing the correct statement:
The traditional financial ratios that analysts use to study a health plan's GAAP-based financial statements include liquidity ratios, activity ratios, leverage ratios, and profitability ratios. Of these categories of ratios, analysts are most likely to use
The Norton Health Plan used blended rating to develop a premium rate for the Roswell Company, a large employer group. Norton assigned Roswell a credibility factor of 0.7 (or 70%). Norton calculated Roswell’s manual rate to be $200 and its experience claims cost as $180. Norton’s retention charge is $3. This information indicates that Roswell’s blended rate is:
The Jamal Health Plan operates in a state that mandates that a health plan either allow providers to become part of its network or reimburse those providers at the health plan’s negotiated-contract rate, so long as the non-contract provider is willing to perform the services at the contract rate. This type of law is known as:
The Rathbone Company has contracted with the Jarvin Insurance Company to provide healthcare benefits to its employees. Under this contract, Rathbone assumes financial responsibility for paying 80% of its estimated annual claims and for depositing the funds necessary to pay these claims into a bank account. Although Rathbone owns the bank account, Jarvin, acting as Rathbone’s agent, makes the actual claims payments from this account. Claims in excess of Rathbone’s contracted percentage are paid by Jarvin. Rathbone pays to Jarvin a premium for administering the entire plan and bearing the costs of claims in excess of Rathbone’s obligation. This premium is substantially lower than would be charged if Jarvin were providing healthcare coverage under a traditional fully insured group plan. Jarvin is required to pay premium taxes only on the premiums it receives from Rathbone. This information indicates that the type of alternative funding method used by Rathbone is known as a:
The goal of the investment department at the Wayfarer Health Plan is to maximize investment return. The investment department executes investments on time and at a low cost. However, these transactions often result in low returns or risks that are deemed too high for Wayfarer. With regard to effectiveness and efficiency, it is correct to say that Wayfarer’s investment department is:
In order to print all of its forms in-house, the Prism health plan is considering the purchase of 10 new printers at a total cost of $30,000. Prism estimates that the proposed printers have a useful life of 5 years. Under its current system, Prism spends $10,000 a year to have forms printed by a local printing company. Assume that Prism selects a 15% discount rate based on its weighted-average costs of capital. The cash inflows for each year, discounted to their present value, are shown in the following chart:
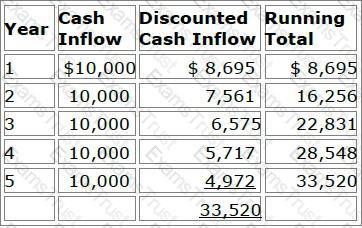
Prism will use both the payback method and the discounted payback method to analyze the worthiness of this potential capital investment. Prism's decision rule is to accept all proposed capital projects that have payback periods of four years or less.
Now assume that Prism decides to use the net present value (NPV) method to evaluate this potential investment's worthiness and that Prism will accept the project if the project's NPV is greater than $4,000. Using the NPV method, Prism would correctly conclude that this project should be
The Puma health plan uses return on investment (ROI) and residual income (RI) to measure the performance of its investment centers. Two of these investment centers are identified as X and Y. Investment Center X earns $10,000,000 in operating income on controllable investments of $50,000,000, and it has total revenues of $60,000,000. Investment Center Y earns $2,000,000 in operating income on controllable investments of $8,000,000, and it has total revenues of $10,000,000. Both centers have a minimum required rate of return of 15%.
The following statements are about Puma's evaluation of these investment centers. Select the answer choice containing the correct statement.
Residual trend is the difference between total trend and the portion of the total trend caused by changes in provider reimbursement levels.
Consider the following events that could affect an health plan’s provider reimbursement levels:
Event 1 — The disenrollment of a large group with unusually high utilization rates
Event 2 — The introduction of a new treatment for infertility
Event 3 — A serious flu epidemic
Event 4 — A shift in inpatient medical services from obstetrical care to neonatal intensive care
One cause of residual trend is change in intensity, which would be represented by:
Juan Ramirez, a licensed social worker, and Dr. Laura Lui, a licensed psychiatrist, are under contract to the Peninsula Health Plan. Peninsula has contracted with CMS to provide services to Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. Both Mr. Ramirez and Dr. Lui provide the same type of counseling services to Peninsula's enrollees. With respect to amendments made to the Balanced Budget Act (BBA) of 1997 that impact provider reimbursement, the amount by which Peninsula will reimburse Mr. Ramirez will be equal to:
The following transactions occurred at the Lane Health Plan:
Of these transactions, the one that is consistent with the accounting principle of conservatism is:
The Landau health plan will switch from using top-down budgeting to using bottom-up budgeting. One potential advantage to Landau of making this switch is that, compared to top-down budgeting, bottom-up budgeting is more likely to
In evaluating the claims experience during a given rating period of the Lucky Company, the Calaway Health Plan determined that the claims incurred by Lucky were lower than Calaway anticipated when it established Lucky’s premium rate for the rating period. Calaway, therefore, refunded a portion of Lucky’s premium to reflect the better-than-anticipated claims experience. This rating method is known as:
Ways in which a company can increase its return on investment (ROI) include:
1. Reducing expenses to increase operating income
2. Increasing controllable investment
Contingency risks, or C-risks, are general categories of risk that have a direct bearing on both the cash flow and solvency of a health plan. One of these C-risks, pricing risk (C-2 risk), is typically the most important risk a health plan faces. Pricing risk is crucial to a health plan’s solvency because:
The following statements are about the capital budgeting technique known as the payback method. Select the answer choice containing the correct statement:
The Fiesta Health Plan prices its products in such a way that the rates for its products are reasonable, adequate, equitable, and competitive. Fiesta is using blended rating to calculate a premium rate for the Murdock Company, a large employer. Fiesta has assigned a credibility factor of 0.6 to Murdock. Fiesta has also determined that Murdock's manual rate is $200 PMPM and that Murdock's experience rate is $180 PMPM.
According to regulations, Fiesta's premium rates are reasonable if they
The Sanford Group, a provider group, entered into a risk contract with a health plan. Sanford has purchased aggregate stop-loss coverage with an attachment point of 115% of the group's predicted healthcare costs of $2,000,000 for the year. Sanford has a copayment of 10% for any costs above the attachment point. If Sanford's actual costs for the year are $2,800,000, then, according to the terms of the aggregate stop-loss agreement, the amount that Sanford is responsible for is
For each of its products, the Wisteria Health Plan monitors the provider reimbursement trend and the residual trend. One true statement about these trends is that
The following statements illustrate the use of different rating methods by health plans:
From the following answer choices, select the response that correctly indicates the rating methods used by Dover and Rolling Hills.
The Eagle health plan wants to limit the possibility that it will be held vicariously liable for the negligent acts of providers. Dr. Michael Chan is a member of an independent practice association (IPA) that has contracted with Eagle. One step that Eagle could take in order to limit its exposure under the theory of vicarious liability is to
The Caribou health plan is a for-profit organization. The financial statements that Caribou prepares include balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. To prepare its cash flow statement, Caribou begins with the net income figure as reported on its income statement and then reconciles this amount to operating cash flows through a series of adjustments. Changes in Caribou's cash flow occur as a result of the health plan's operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
The basic formula for Caribou's income statement is
Experience rating and manual rating are two rating methods that the Cheshire health plan uses to determine its premium rates. One difference between these two methods is that, under experience rating, Cheshire
The Challenger Group is a type of management services organization (MSO) that purchases the assets of physician practices, provides practice management and administrative support services to participating providers, and offers physicians a long-term contract and an equity position in Challenger. This information indicates that Challenger is a type of health plan
Health plans seeking to provide comprehensive healthcare plans must contract with a variety of providers for ancillary services. One characteristic of ancillary services is that
Three general strategies that health plans use for controlling types of risk are risk avoidance, risk transfer, and risk acceptance. The following statements are about these strategies. Three of these statements are true, and one statement is false. Select the answer choice containing the FALSE statement.
The Kayak Company self funds the health plan for its employees. This plan is an example of a type of self-funded plan known as a general asset plan. The fact that this is a completely self-funded plan indicates that
In the following paragraph, a sentence contains two pairs of words enclosed in parentheses. Determine which word in each pair correctly completes the statement. Then select the answer choice containing the two words that you have selected.
The Igloo health plan recognizes the receipt of its premium income during the accounting period in which the income is earned, regardless of when cash changes hands. However, Igloo recognizes its expenses when it earns the revenues related to those expenses, regardless of when it receives cash for the revenues earned. This information indicates that the (realization/capitalization) principle governs Igloo's revenue recognition, whereas the (matching/initial-recording) principle governs its expense recognition.
With regard to the major risk factors associated with group underwriting, it can correctly be stated that, typically,
The Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Model Act, developed by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), represents one approach to developing solvency standards. One drawback to this type of solvency regulation is that it
The Violin Company offers its employees a triple option of health plans: an HMO, an HMO with a point of service (POS) option, and an indemnity plan.
Premiums are lowest for the HMO option and highest for the indemnity plan. Violin employees who anticipate that they will be individual low utilizes of healthcare services are most likely to enroll in the
The following statements illustrate common forms of capitation:
1. The Antler Health Plan pays the Epsilon Group, an integrated delivery system (IDS), a capitated amount to provide substantially all of the inpatient and outpatient services that Antler offers. Under this arrangement, Epsilon accepts much of the risk that utilization rates will be higher than expected. Antler retains responsibility for the plan's marketing, enrollment, premium billing, actuarial, underwriting, and member services functions.
2. The Bengal Health Plan pays an independent physician association (IPA) a capitated amount to provide both primary and specialty care to Bengal's plan members. The payments cover all physician services and associated diagnostic tests and laboratory work. The physicians in the IPA determine as a group how the individual physicians will be paid for their services.
From the following answer choices, select the response that best indicates the form of capitation used by Antler and Bengal.